
what you'll learn...
Overview
Position Vector of a Point
» For a point the position vector is
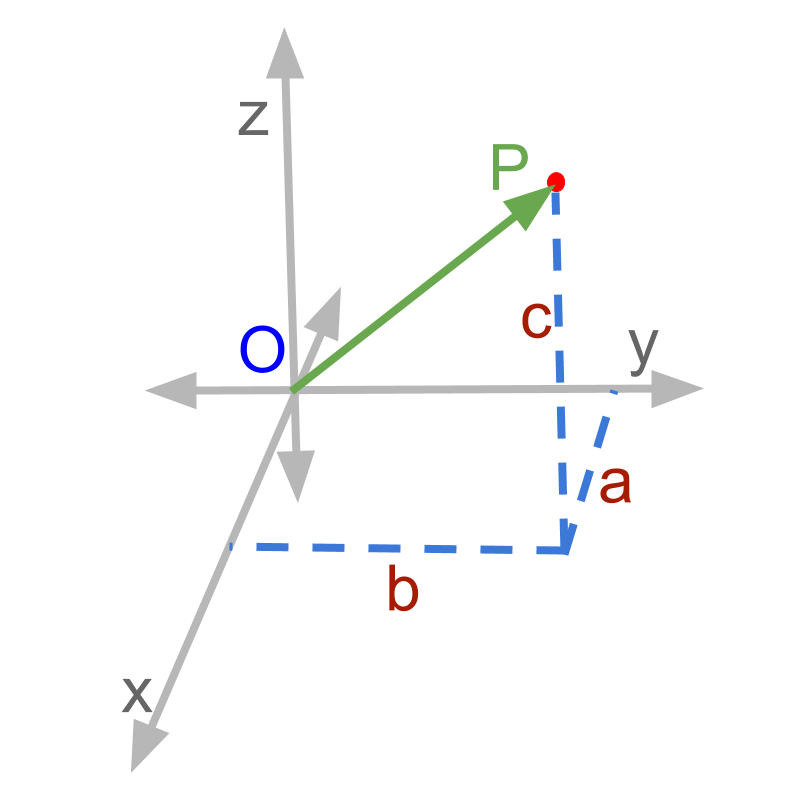
position means place

Consider a point in 3D coordinate system as shown in figure. The point is given by the following.
in 3D coordinates it is
as a vector representation
as the vector
The word 'position' means 'place; location'.
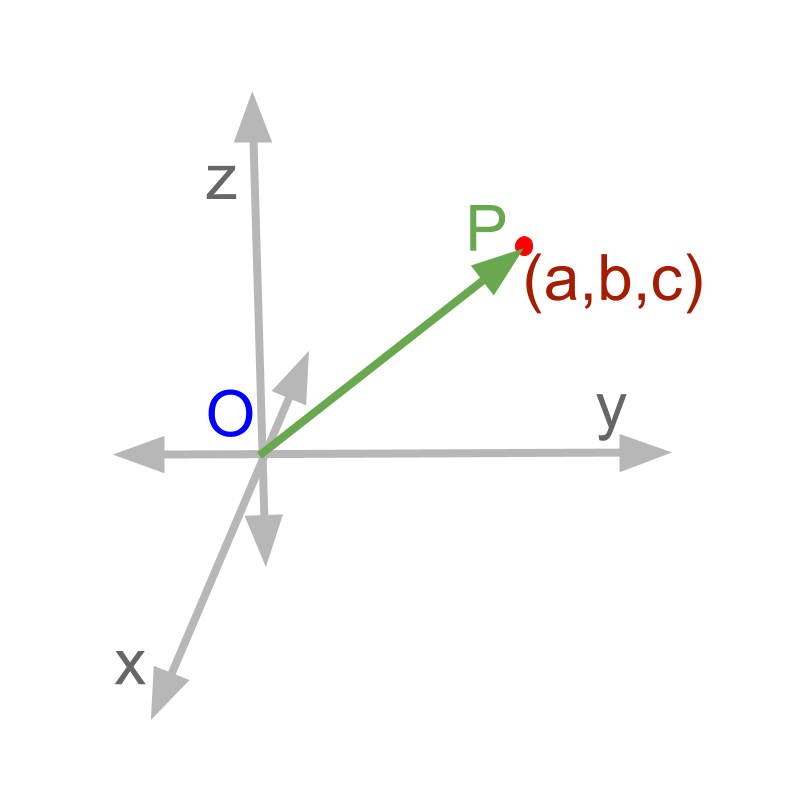
Given a point as shown in figure. Position vector of a point is
Position Vector: For a point the position vector is
.
Position Vector of a Point is the vector between origin and the point.
examples
What is the position vector of point ?
The answer is ''.
Given the vector , if is the origin, what is the coordinate position of point ?
The answer is ''
What is the position vector of point ?
The answer is ''.
summary

Position Vector: For a point the position vector is
.
Outline
The outline of material to learn vector-algebra is as follows.
Note: Click here for detailed outline of vector-algebra.
• Introduction to Vectors
→ Introducing Vectors
→ Representation of Vectors
• Basic Properties of Vectors
→ Magnitude of Vectors
→ Types of Vectors
→ Properties of Magnitude
• Vectors & Coordinate Geometry
→ Vectors & Coordinate Geometry
→ Position Vector of a point
→ Directional Cosine
• Role of Direction in Vector Arithmetics
→ Vector Arithmetics
→ Understanding Direction of Vectors
• Vector Addition
→ Vector Additin : First Principles
→ Vector Addition : Component Form
→ Triangular Law
→ Parallelogram Law
• Multiplication of Vector by Scalar
→ Scalar Multiplication
→ Standard Unit Vectors
→ Vector as Sum of Vectors
→ Vector Component Form
• Vector Dot Product
→ Introduction to Vector Multiplication
→ Cause-Effect-Relation
→ Dot Product : First Principles
→ Dot Product : Projection Form
→ Dot Product : Component Form
→ Dot Product With Direction
• Vector Cross Product
→ Vector Multiplication : Cross Product
→ Cross Product : First Principles
→ Cross Product : Area of Parallelogram
→ Cross Product : Component Form
→ Cross Product : Direction Removed