
what you'll learn...
Overview
Measurement by Superimposition : Length, Area, or Volume can be measured by superimposition of corresponding unit-measures.
overlay a grid
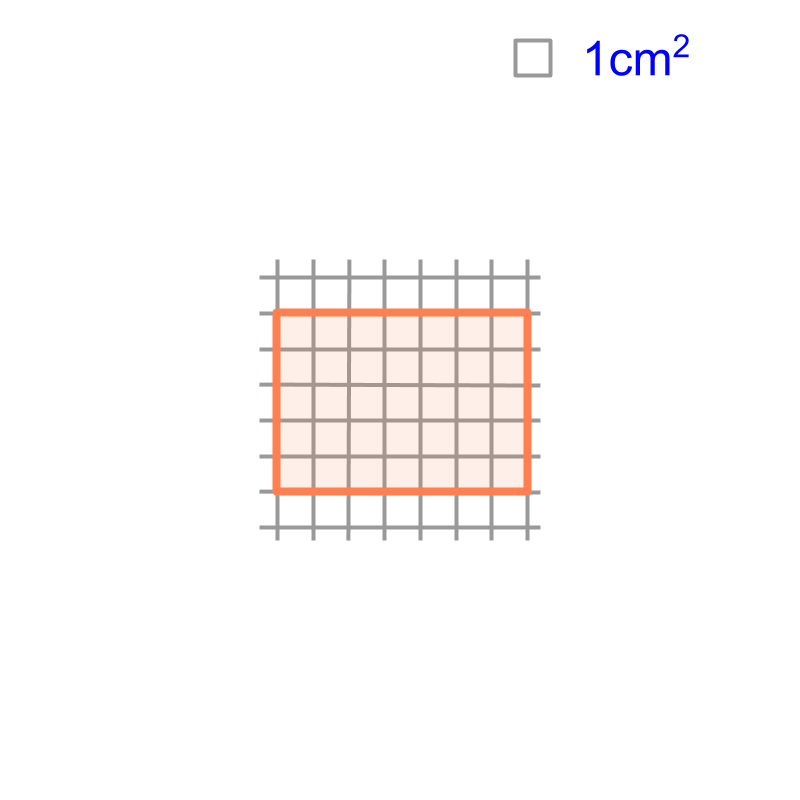
Consider the shape given in the figure. It is a rectangle of length cm and width cm. 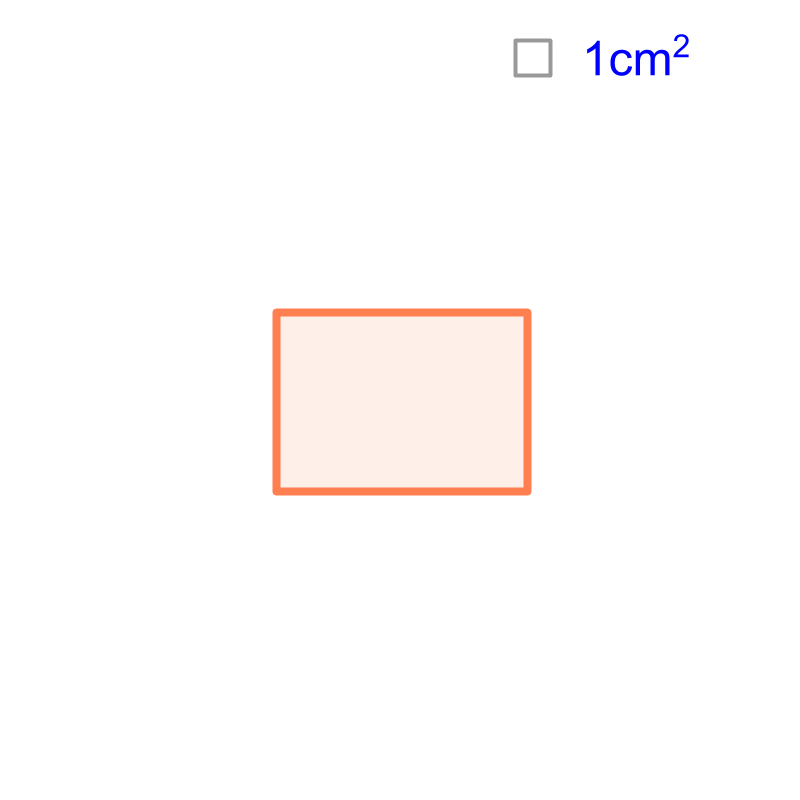 The figure also provides the reference unit-square on the top-right. The area of the shape is "". The area is computed by creating a grid of unit-squares. The number of unit squares contained within the shape is the area of the rectangle.
The figure also provides the reference unit-square on the top-right. The area of the shape is "". The area is computed by creating a grid of unit-squares. The number of unit squares contained within the shape is the area of the rectangle.

simplify
Area of the given shape is calculated by superimposing the reference unit-squares. Based on this, the area of a square or rectangle is simplified to the formulas
approximate
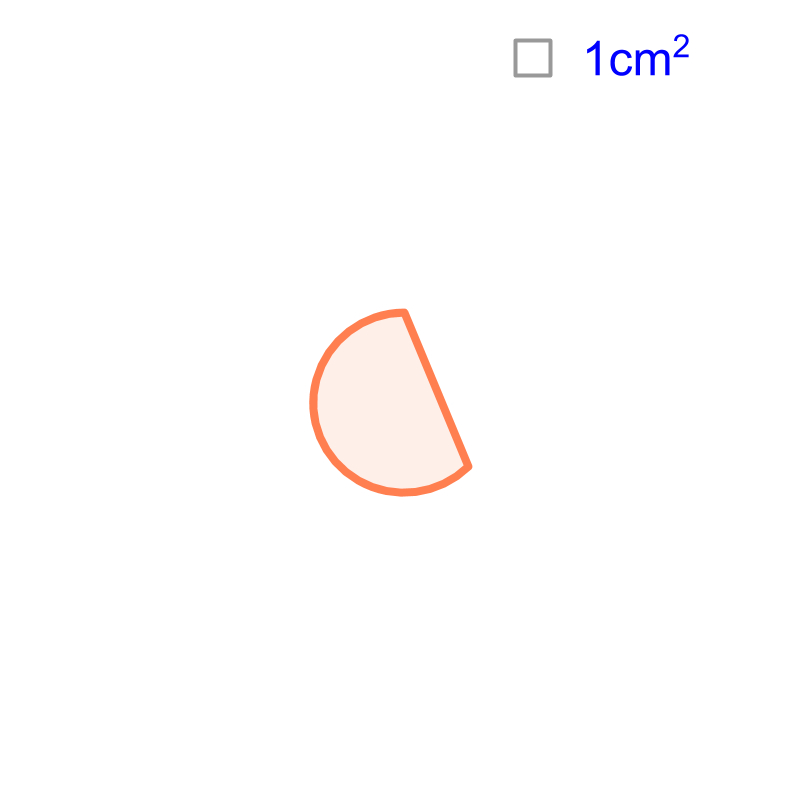
Consider the shape given in the figure. The measurements are not provided. The reference unit-square is shown on the top-right corner. Can we calculate the area of the given shape? Yes, "approximate area can be calculated by superimposing a grid of unit-squares".
The area is approximately .
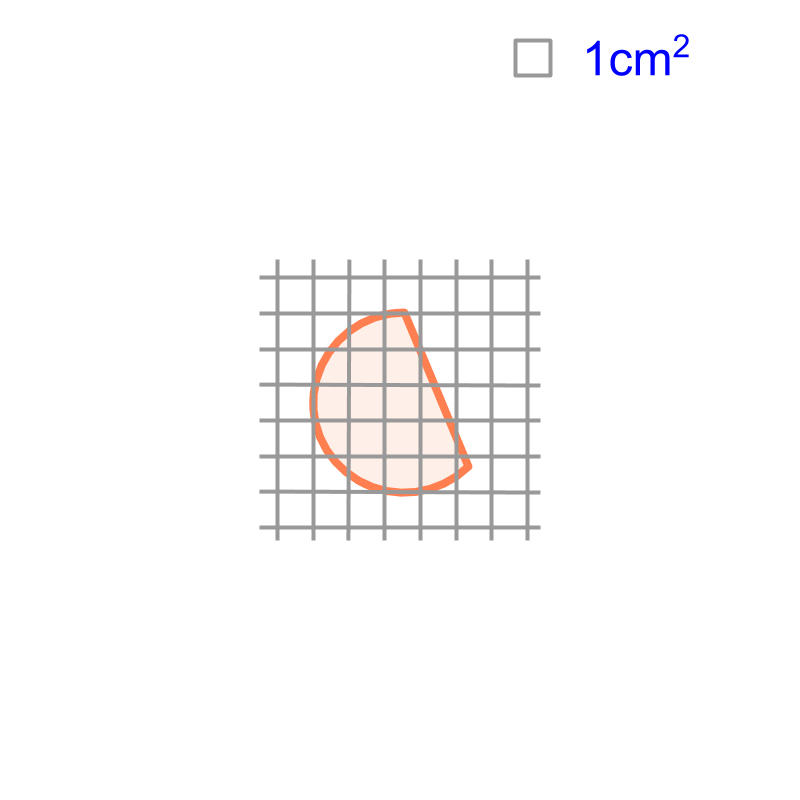 .
.
The area is approximated to the count of large squares within the figure.
suitable for some shapes
Measurement by superimposition provides accurate results for
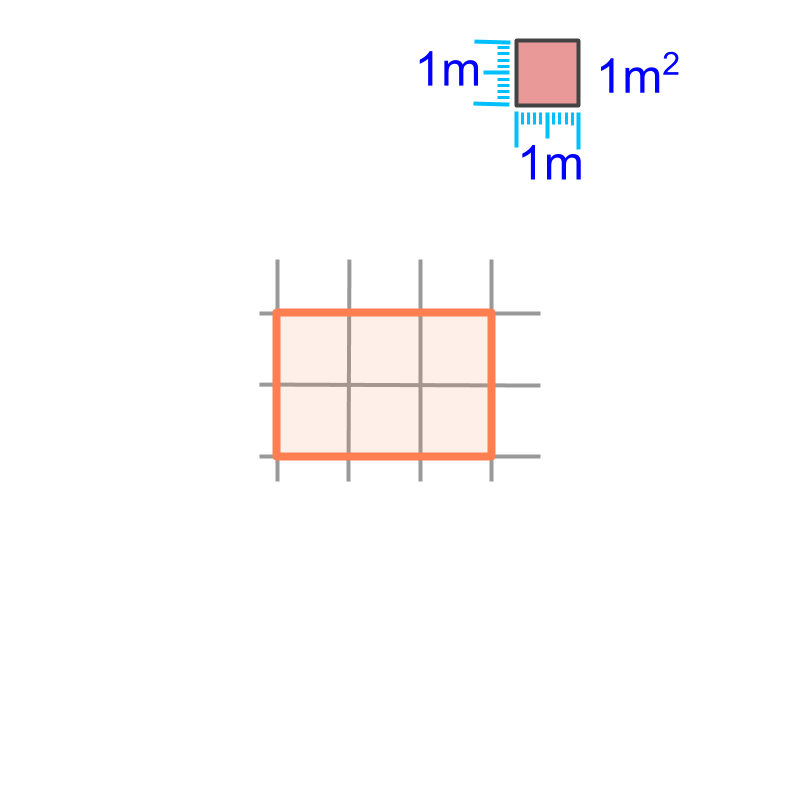
• area of squares and rectangles : The unit-square has angles at the vertices. And so, the unit-square fits within Squares and Rectangles.
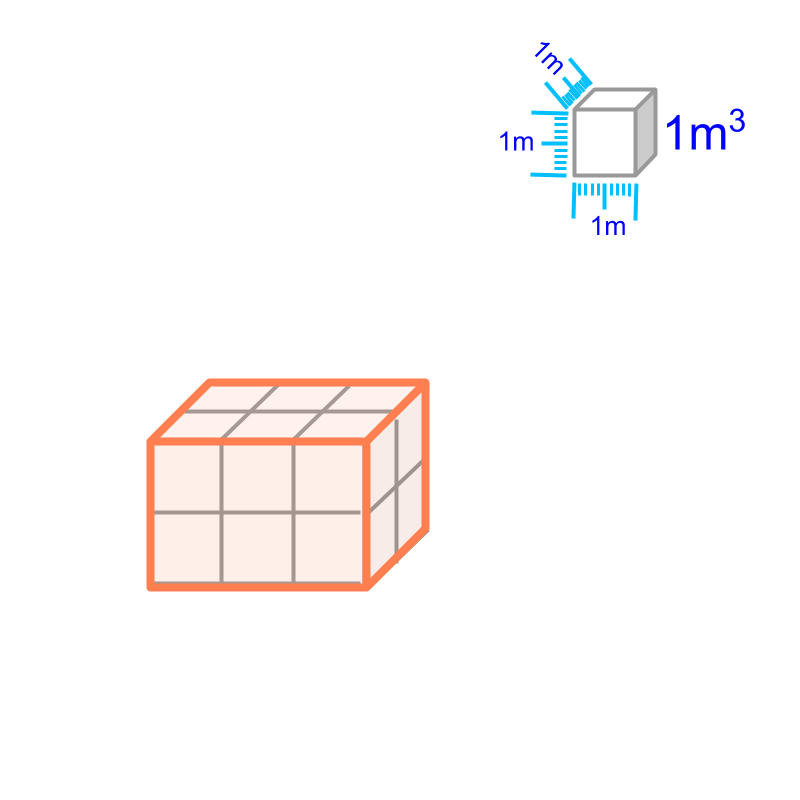
• volume of cubes and cuboids : The unit-cube has angles at the vertices. And so, the unit-cube fits within cubes and cuboids.
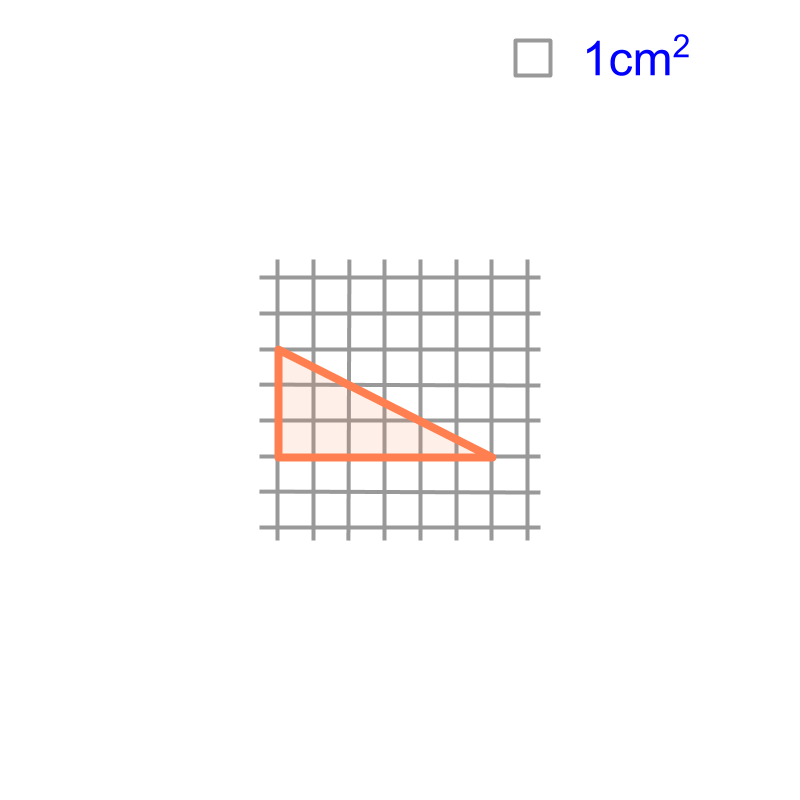
For shapes like triangles or prisms, measurement requires some geometrical calculation or the measurement will be approximate.
summary
Measurement by Superimposition : Length, Area, or Volume can be measured by superimposition of corresponding unit-measures.
 This method suits best for
This method suits best for
• area of squares and rectangles
• volume of cubes and cuboids
Outline
The outline of material to learn Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume is as follows.
Note 1: click here for the detailed overview of Mensuration High
Note 2: click here for basics of mensuration, which is essential to understand this.
• Basics of measurement
→ Summary of Measurement Basics
→ Measurement by superimposition
→ Measurement by calculation
→ Measurement by equivalence
→ Measurement by infinitesimal pieces
→ Cavalieri's Principle (2D)
→ Cavalieri's Principle (3D)
• Perimeter & Area of 2D shapes
→ Circumference of Circles
→ Area of Circles
• Surface area & Volume of 3D shapes
→ Prisms : Surface Area & Volume
→ Pyramids : Surface Area & Volume
→ Cone : Surface Area & Volume
→ Sphere : Surface Area & Volume
• Part Shapes
→ Understanding part Shapes
→ Circle : Sector and Segment
→ Frustum of a Cone