
what you'll learn...
Overview
We studied about 2D shapes
• squares,
• rectangles,
• triangles,
• polygons, and
• circles
These are some of the standard shapes.
Some part-shapes can be derived from these standard shapes. One of the method is to cut the shapes with straight lines and part of the standard shape is analyzed for perimeter or area.
The following are studied
 • the perimeter and area of sectors and segments.
• the perimeter and area of sectors and segments.
 • the surface area and volume of frustum.
• the surface area and volume of frustum.
slicing rectangle
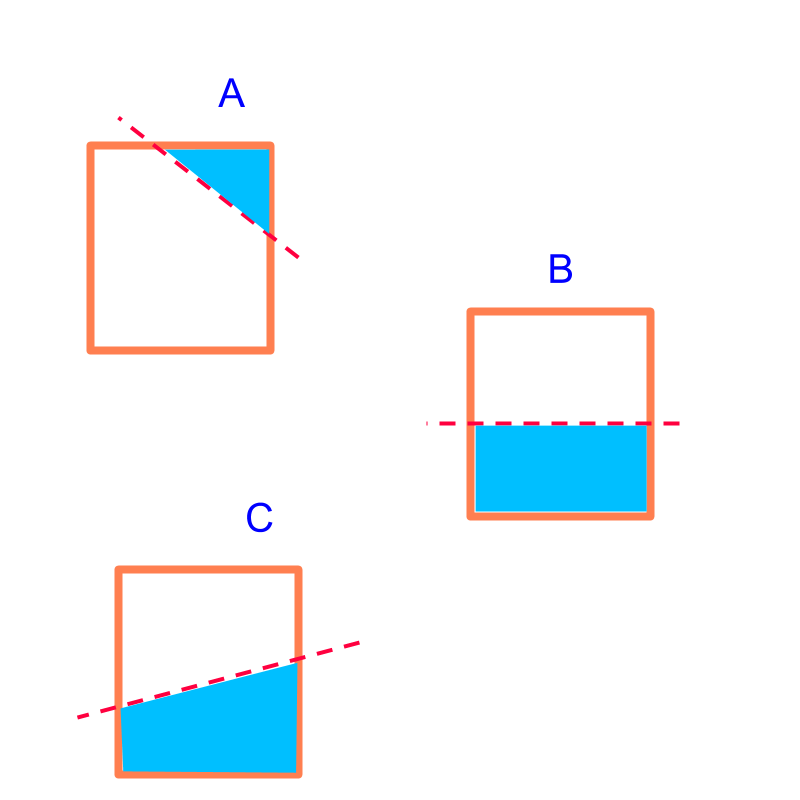
Consider slicing rectangle as shown in the figure. The possible shapes formed in slicing a rectangle with a straight line are
triangle
rectangle
or
quadrilateral.
Part shapes are illustrated in the figure.
It is noted that for polygons, the part-shape will be another polygon.
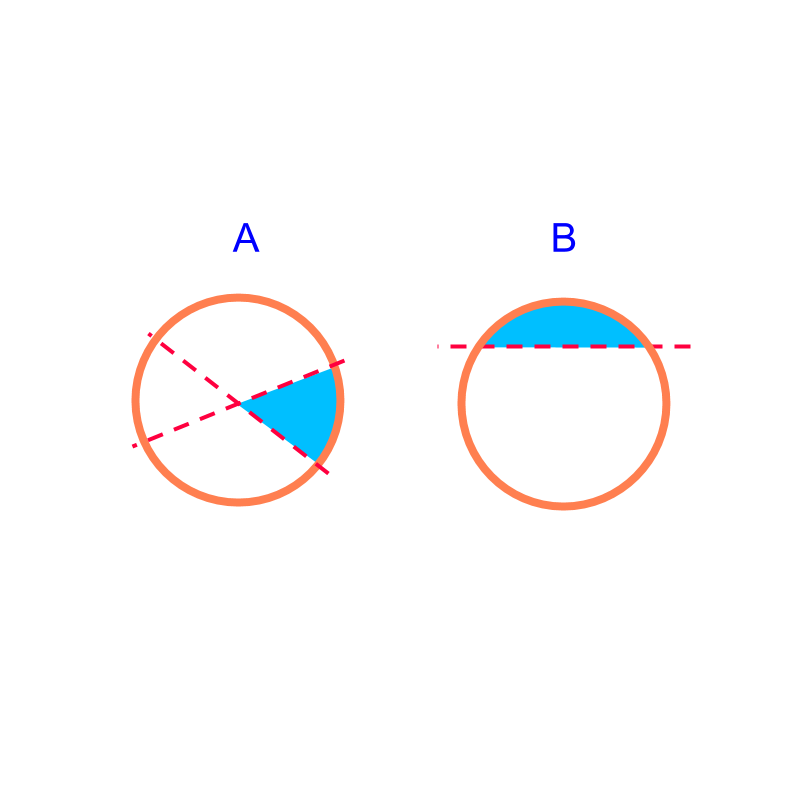
slicing circle

When a circle is sliced with a line, the shapes formed are "sector and segment", as shown in the figure.
Sector and Segment are studied in Geometry. In mensuration, the interest is in finding the perimeter and area of the part-shapes. In particular, the perimeter and area of sectors and segments are studied.
solids
We studied about 3D solids
• cubes,
• cuboids,
• cylinders,
• cones,
• prisms,
• pyramids, and
• spheres
These are some of the standard solids.
Some part-solids can be derived from these standard shapes. One of the method is to cut the shapes with a plane and part of the standard shape is analyzed for surface area or volume.
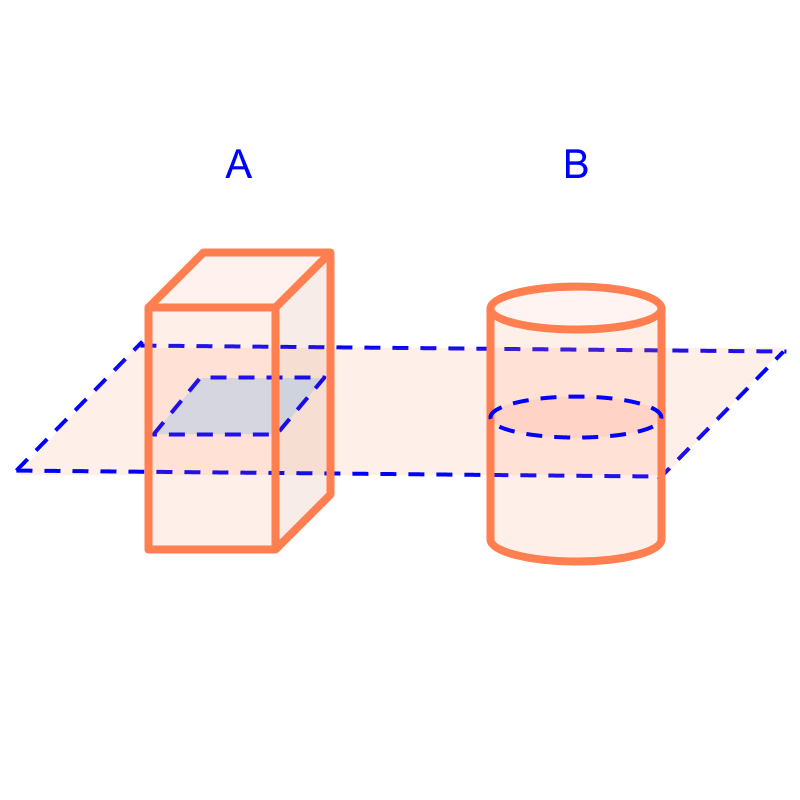
Consider slicing a cuboid and a cylinder with a plane as shown in the figure. For this course, we restrict ourselves to planes parallel to one of the faces. The part-solids are formed from this are a cuboid and a cylinder.
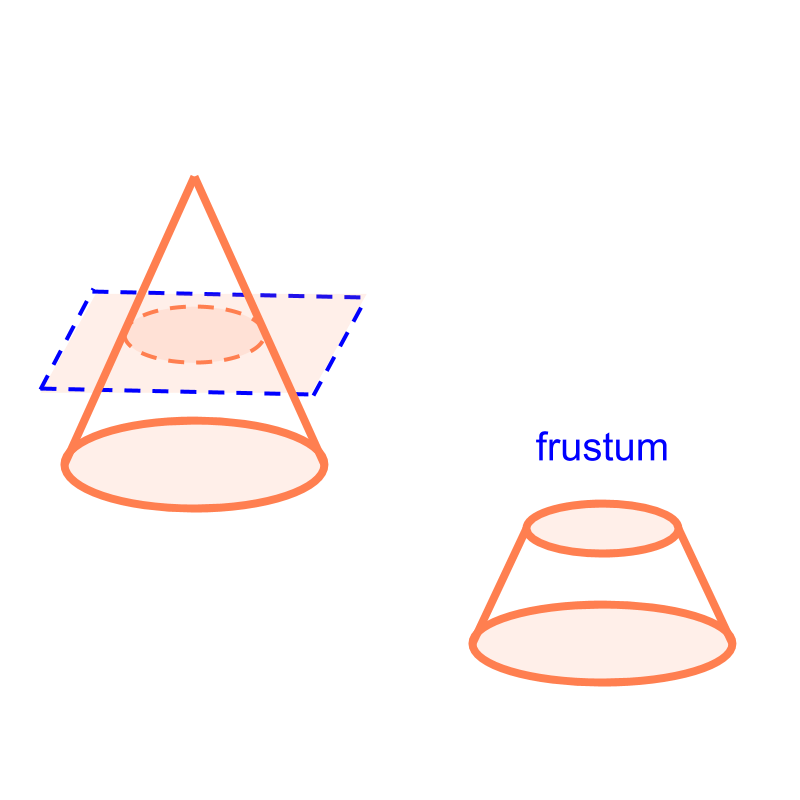
slicing cone

When a cone is sliced with a plane, the part-solid formed are shown in the figure. The two part-solids of cone are a cone and a frustum
summary
The part-shaped formed by planes, that are not parallel to a face of the solid, are outside the scope of this course. In mensuration, the interest is in finding the surface area and volume of the part-shapes. In particular, the following are studied
 • the perimeter and area of sectors and segments.
• the perimeter and area of sectors and segments.
 • the surface area and volume of frustum.
• the surface area and volume of frustum.
Outline
The outline of material to learn Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume is as follows.
Note 1: click here for the detailed overview of Mensuration High
Note 2: click here for basics of mensuration, which is essential to understand this.
• Basics of measurement
→ Summary of Measurement Basics
→ Measurement by superimposition
→ Measurement by calculation
→ Measurement by equivalence
→ Measurement by infinitesimal pieces
→ Cavalieri's Principle (2D)
→ Cavalieri's Principle (3D)
• Perimeter & Area of 2D shapes
→ Circumference of Circles
→ Area of Circles
• Surface area & Volume of 3D shapes
→ Prisms : Surface Area & Volume
→ Pyramids : Surface Area & Volume
→ Cone : Surface Area & Volume
→ Sphere : Surface Area & Volume
• Part Shapes
→ Understanding part Shapes
→ Circle : Sector and Segment
→ Frustum of a Cone