
what you'll learn...
Overview
Area of a Circle : Circumference of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is represented by the symbol
Area of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is taken to be another value . It can be calculated to be a value by approximating the circle to infinitesimally small triangular pieces.
 We derive / prove that
We derive / prove that
Area of a circle of cm radius is computed to be times the area of the circle of cm diameter.
Thus the generic formula for the area of a circle is
recap
We have learned the following
• Length of a real-life object or a line can be a decimal number in which the decimals do not end or do not repeat.
• Circumference of a circle is times the diameter.
Similarly, the area of a circle of cm radius is also a decimal number in which the decimals do not end or repeat. It is calculated that the area of a circle or radius is or .
The above was at beginner level understanding. Now, let us learn how to calculate the area of a circle .
calculating
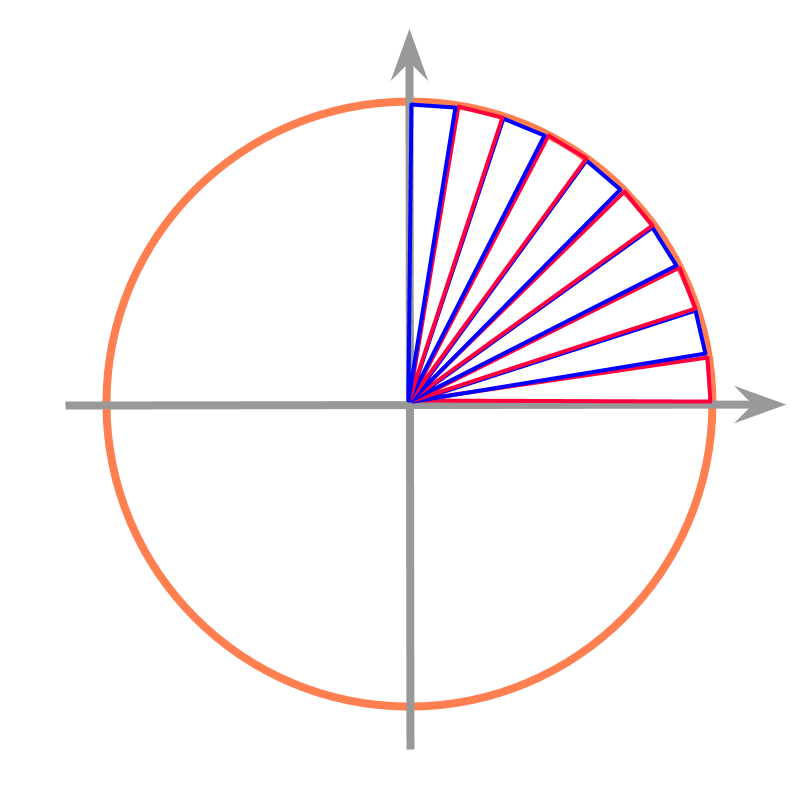
Consider the circle given in the figure. The diameter of the circle is cm. We visualize the circle as a combination of isosceles-triangles and find sum of the area of triangles as the approximate area of the circle.

One of the triangles from the above is isolated and shown along with the corresponding arc of the circle. 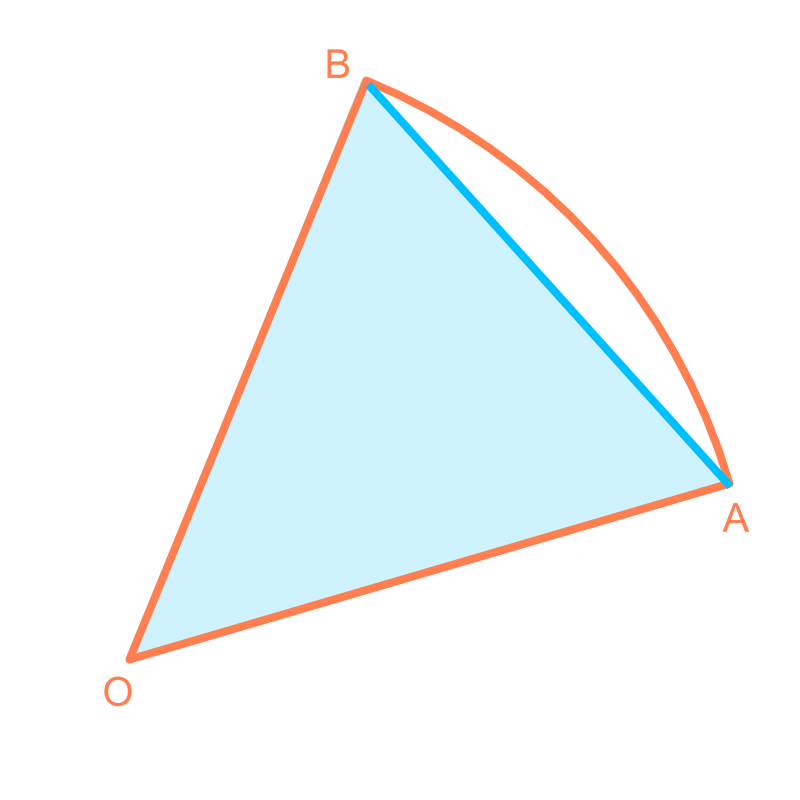
The area of the triangle is an approximation to the corresponding sector of the circle .
To increase the accuracy of the area the triangles are made thinner (angle between equal sides is smaller).
The area of a circle is calculated by one of many methods involving equivalence and approximation.
The area of the circle is the sum of area of the isosceles triangles.
sum of
As the triangles are made infinitesimal,
• the height of the triangle is the radius and
• the sum of bases is the perimeter
So the area is
summarizing the derivation
Circumference of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is represented by the symbol
Area of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is taken to be another value
We drived that
Area of a circle of cm radius is computed to be times the area of the circle of cm diameter.
Thus the generic formula for the area of a circle is
What is the area of a circle of cm radius?
The answer is "".
Area
summary
Area of a Circle :
Circumference of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is represented by the symbol
Area of a circle of cm diameter is computed to be a decimal value that does not end or repeat. That accurate value is taken to be another value . It can be calculated to be a value by approximating the circle to infinitesimally small triangular pieces.
 We derive / prove that
We derive / prove that
Area of a circle of cm radius is computed to be times the area of the circle of cm diameter.
Thus the generic formula for the area of a circle is
Outline
The outline of material to learn Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume is as follows.
Note 1: click here for the detailed overview of Mensuration High
Note 2: click here for basics of mensuration, which is essential to understand this.
• Basics of measurement
→ Summary of Measurement Basics
→ Measurement by superimposition
→ Measurement by calculation
→ Measurement by equivalence
→ Measurement by infinitesimal pieces
→ Cavalieri's Principle (2D)
→ Cavalieri's Principle (3D)
• Perimeter & Area of 2D shapes
→ Circumference of Circles
→ Area of Circles
• Surface area & Volume of 3D shapes
→ Prisms : Surface Area & Volume
→ Pyramids : Surface Area & Volume
→ Cone : Surface Area & Volume
→ Sphere : Surface Area & Volume
• Part Shapes
→ Understanding part Shapes
→ Circle : Sector and Segment
→ Frustum of a Cone