
what you'll learn...
Overview
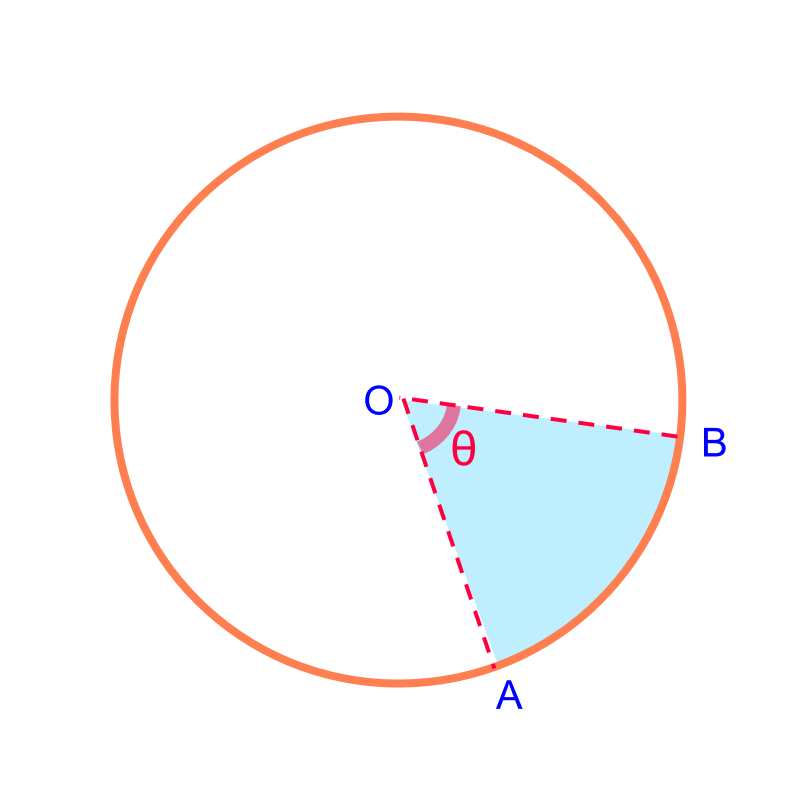 Arc Length and Area of a Sector: The arc-length and area are proportion to the angle subtended by the sector.
Arc Length and Area of a Sector: The arc-length and area are proportion to the angle subtended by the sector.
Arc length of a sector of angle
Area of a sector of angle
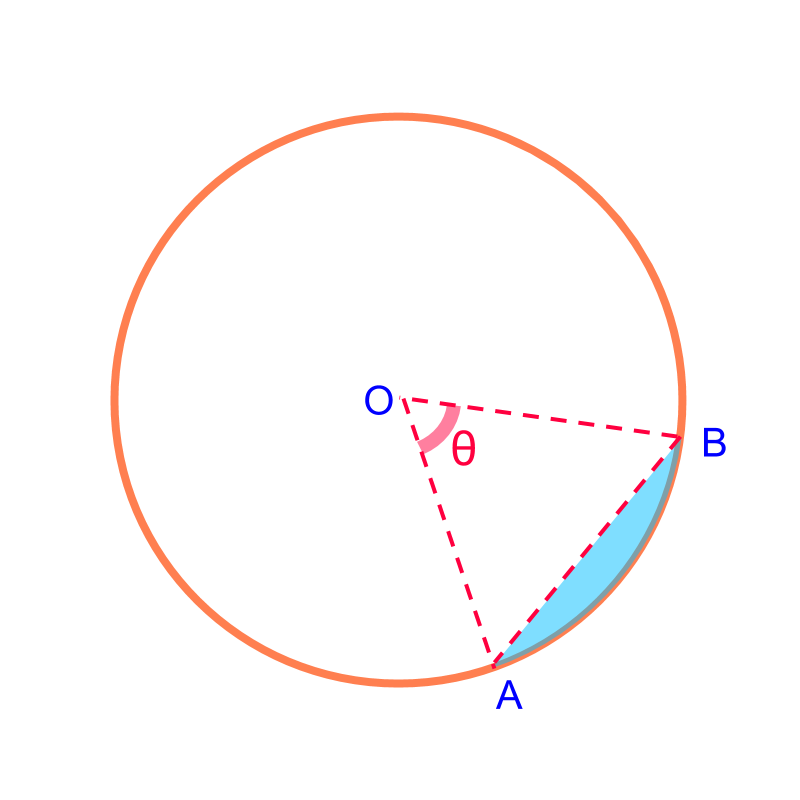 Area of a Segment: is the difference between area of sector and the triangle.
Area of a Segment: is the difference between area of sector and the triangle.
Area of a Segment of angle = area of the corresponding sector the triangle
recap circle
The perimeter and area of a circle of radius is " and "
The angle subtended by a circle on the center is ""
sector

Consider the sector of a circle shown in the figure. The parameters required to define the sector are "the radius and the angle subtended by the sector"
We learned that
Perimeter of a circle is
Area of a circle is
Angle subtended by the entire circle is
By the symmetry in the circle, it is found that the sector of angle has
Arc length of a sector of is . That is, the ratio of angle of the sector to full-angle is the ratio of perimeter of the sector to that of the full-circle.
Area of a sector of is . That is, the ratio of angle of the sector to full-angle is the ratio of area of the sector to that of the full-circle.
measures of sector

Consider the sector given in figure. The arc length of minor arc is ""
The perimeter of the shaded sector is curve plus two radius length =
The area of the shaded sector is "".

The area of the shaded segment is "Area of triangle is subtracted from area of sector "
What is the area of a sector of and segment of in a circle?
The answer is "area of sector equals the area of segment "
summary
Arc Length and Area of a Sector:
 The arc-length and area are proportion to the angle subtended by the sector.
The arc-length and area are proportion to the angle subtended by the sector.
Arc length of a sector of angle
Area of a sector of angle
Area of a Segment: is the difference between area of sector and the triangle.
 Area of a Segment of angle = area of the corresponding sector the triangle
Area of a Segment of angle = area of the corresponding sector the triangle
Outline
The outline of material to learn Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume is as follows.
Note 1: click here for the detailed overview of Mensuration High
Note 2: click here for basics of mensuration, which is essential to understand this.
• Basics of measurement
→ Summary of Measurement Basics
→ Measurement by superimposition
→ Measurement by calculation
→ Measurement by equivalence
→ Measurement by infinitesimal pieces
→ Cavalieri's Principle (2D)
→ Cavalieri's Principle (3D)
• Perimeter & Area of 2D shapes
→ Circumference of Circles
→ Area of Circles
• Surface area & Volume of 3D shapes
→ Prisms : Surface Area & Volume
→ Pyramids : Surface Area & Volume
→ Cone : Surface Area & Volume
→ Sphere : Surface Area & Volume
• Part Shapes
→ Understanding part Shapes
→ Circle : Sector and Segment
→ Frustum of a Cone