
what you'll learn...
Overview
Surface Area and Volume of a frustum:
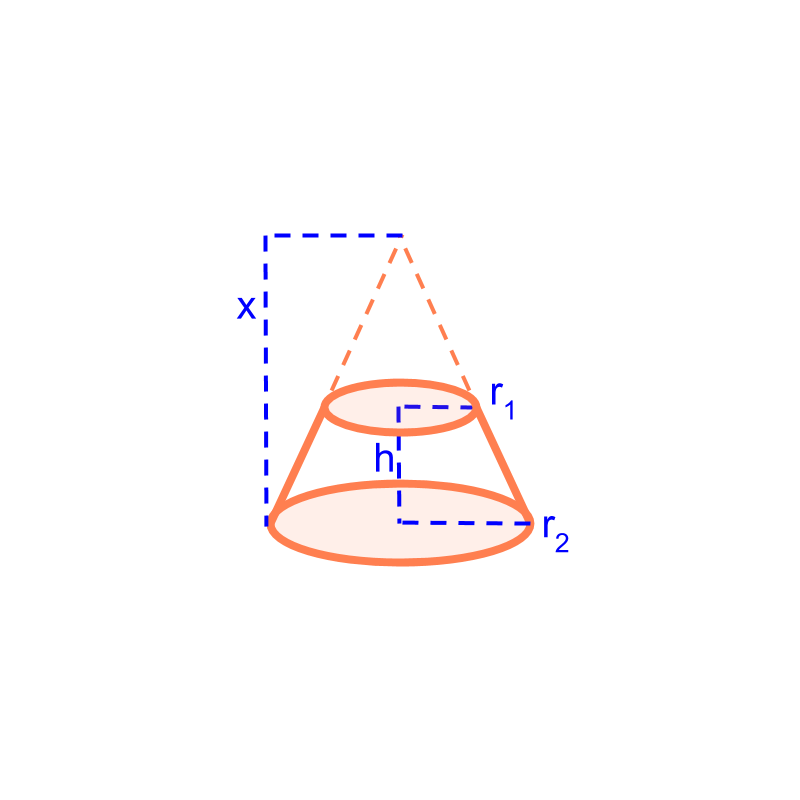 The frustum is visualized as part of a cone and the height of the cone is worked out from the given height and radius of frustum.
The frustum is visualized as part of a cone and the height of the cone is worked out from the given height and radius of frustum.
Surface Area of frustum is the difference between surface area of larger cone and smaller cone.
Volume of frustum is the difference between volume of larger cone and smaller cone.
frustum
The curved surface area of a cone of height and radius is "", where is the slant length
surface area

Consider the frustum with height , radius and .
The figure illustrates the larger cone from which the frustum is formed. The part of the cone sliced is the smaller cone. To find the curved surface area of the frustum, Subtract the surface area of the smaller cone from the surface area of the larger cone. It is noted that the height of the larger cone can be found using the height and the two radius of frustum.
The parameters of the frustum are , and . We have to find the height of larger cone .
It is noted that the and form a side of two similar triangles. The triangles have and as the otherside.
Using the property of similar triangles, it is derived as
Curved surface area of frustum
curved surface area of larger cone - curved surface area of smaller cone
volume
The volume of a cone of height and radius is ""
Consider the frustum with height and radius and .
The figure illustrates the larger cone from which the frustum is formed. The part of the cone sliced is the smaller cone.
To find the volume of the frustum, Subtract the volume of the smaller cone from the volume of the larger cone.
The parameters of the frustum are , and . We have derived the height of larger cone
Volume of frustum
volume of larger cone - volume of smaller cone
What is the volume of a frustum with both top and bottom radius and height ?
It is a cylinder, so volume
As a frustum, the volume , which equals the volume of cylinder.
summary
Surface Area and Volume of a frustum:
 The frustum is visualized as part of a cone and the height of the cone is worked out from the given height and radius of frustum.
The frustum is visualized as part of a cone and the height of the cone is worked out from the given height and radius of frustum.
Surface Area of frustum is the difference between surface area of larger cone and smaller cone.
Volume of frustum is the difference between volume of larger cone and smaller cone.
Outline
The outline of material to learn Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume is as follows.
Note 1: click here for the detailed overview of Mensuration High
Note 2: click here for basics of mensuration, which is essential to understand this.
• Basics of measurement
→ Summary of Measurement Basics
→ Measurement by superimposition
→ Measurement by calculation
→ Measurement by equivalence
→ Measurement by infinitesimal pieces
→ Cavalieri's Principle (2D)
→ Cavalieri's Principle (3D)
• Perimeter & Area of 2D shapes
→ Circumference of Circles
→ Area of Circles
• Surface area & Volume of 3D shapes
→ Prisms : Surface Area & Volume
→ Pyramids : Surface Area & Volume
→ Cone : Surface Area & Volume
→ Sphere : Surface Area & Volume
• Part Shapes
→ Understanding part Shapes
→ Circle : Sector and Segment
→ Frustum of a Cone