
what you'll learn...
Overview
» All shapes of straight lines can be analyzed as combination of right-triangles.
» A right triangle is specified by parameters.
→ 1 parameter (angle) specify "class of similar-right-triangles"
Note: trigonometry is about specifying the ratio of sides in reference to one angle.
→ An additional parameter (a side) specify a right-triangle
Understanding Right Triangles
Before going into details of right angled triangles, students need to understand one application scenario of right angled triangles.
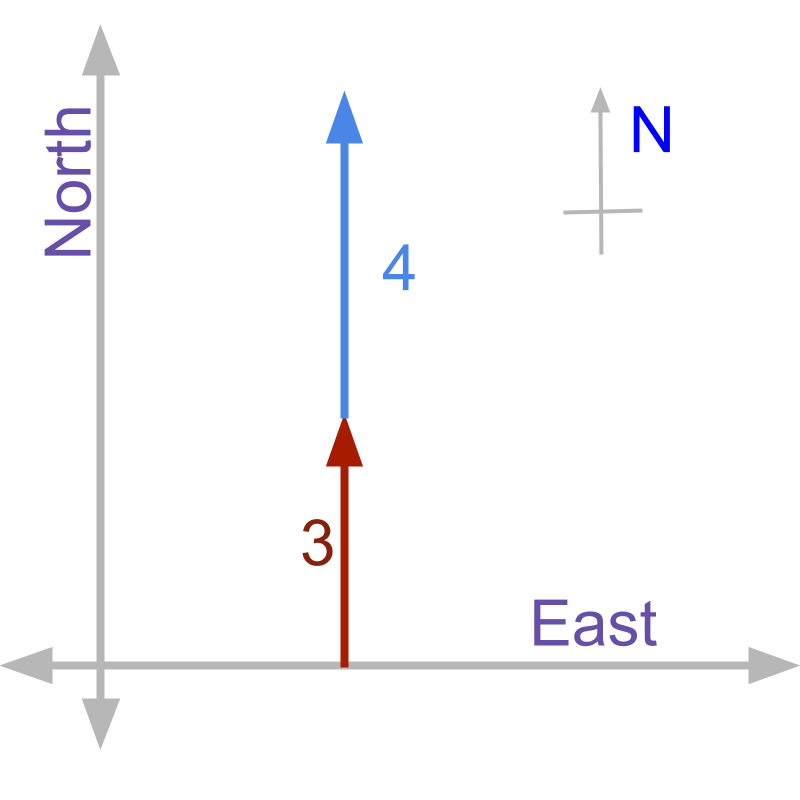
A person walks meter north and continues in the same direction for another meter. The distance he has to walk to return back to the starting position is meter.
Two directional quantities add up in magnitude if they are in same direction.
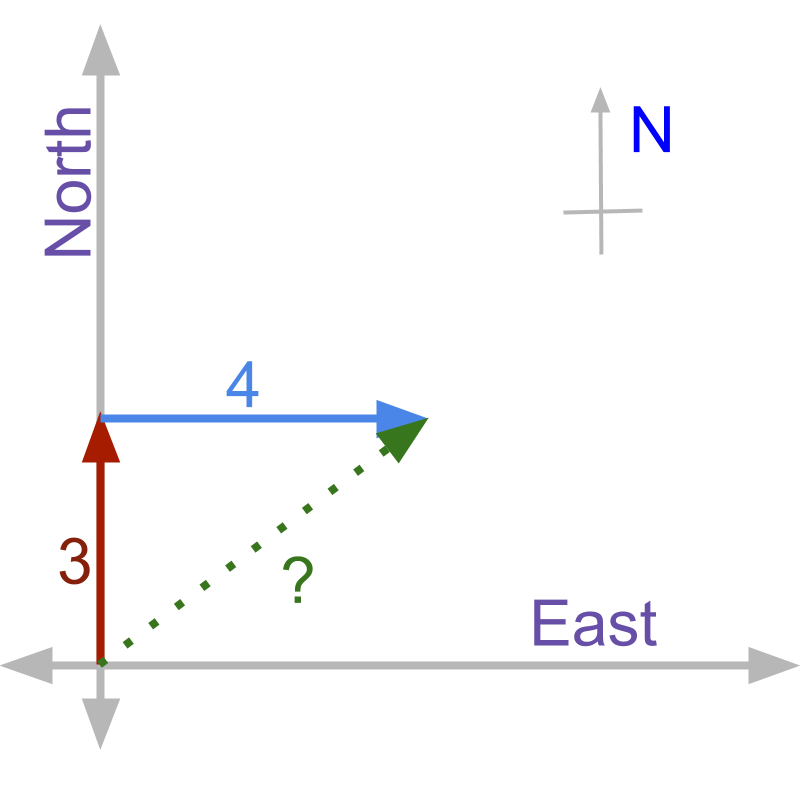
A person walks meter north and continues towards east for another meter. The distance he has to walk to return back to the starting position is not
Two directional quantities do not add up in magnitude if they are not in same direction. The result magnitude will be smaller to the magnitudes of the quantities being added.
Solving a Problem
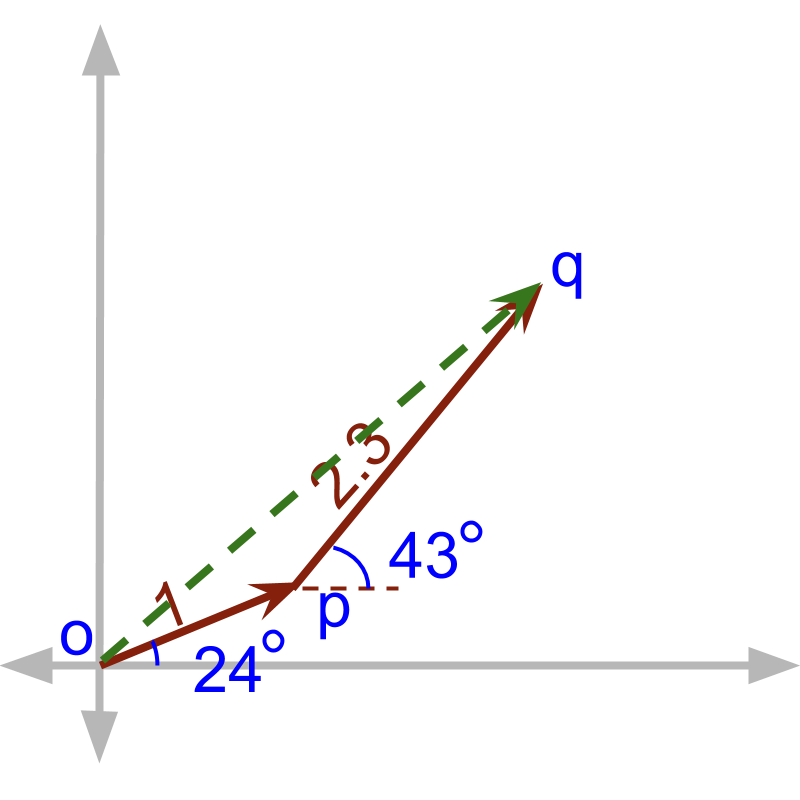
A person walks unit at angle and then continues to walk unit at angle .
The problem is illustrated in figure. To find, the distance he has to walk to return back to the starting position, Principles of right angled triangles can help.
The first walk of unit at is considered as hypotenuse of right angle triangle. The triangle is specified by three parameters 1. right angle 2. given angle 3. length of one side.
The same for the unit at angle , consider that as a right angled triangle. This two can be used to find the sides for the result .
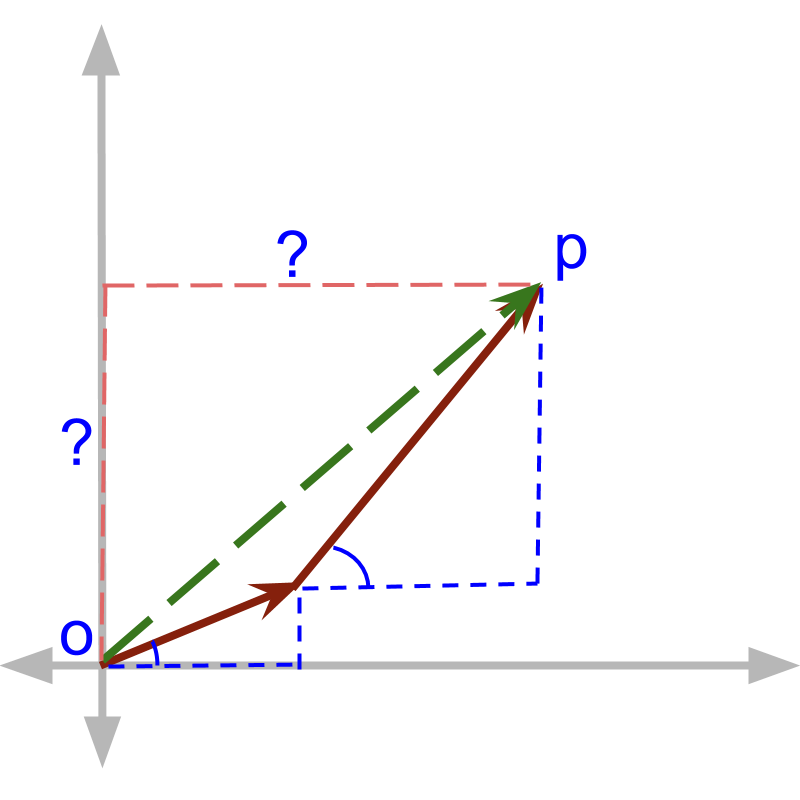
To find the the following steps are followed
Add components along -axis
Add components along -axis
Combine & axes components using Pythagoras theorem
The distances covered at different angles is a good example of directional quantities. Principles and properties of Right angled triangles are useful to solve problems like that.
Other Examples
Where "sides of right angled triangles" are used in practice?
• Area of a quadrilateral is sum of area of two triangles. Any polygon can be handled as sum of triangles.
• Any triangle can be considered as combination of two right angled triangles.
• Directional quantities are best represented in orthogonal components. The orthogonal components are the legs of the right angled triangles.
• Some Directional quantities have their basis in rotational elements. An example is the induced electric current in a wire that rotates in a magnetic field. The angular speed of rotation is constant, and the directional quantity, derived out of it at a given angle , is a leg of the right angled triangle defined by .
• Length of a leg of a right angled triangle, as a function of angle, serves as a mathematical model for analysis.
Students may skip these if these are not easy to understand now. When you use the trigonometry in applications, you may return to refer and understand the above.
Right angled triangles play a significant role in orthogonal components of quantities with directions and orthogonal components of circular rotation.
Summary
Application of Right-Angled-Triangle: Application can be classified into
• orthogonal components of quantities having direction.
• orthogonal components of quantities with circular rotation.
• mathematical model for analysis.
Outline
The outline of material to learn "Basics of Trigonometry" is as follows.
• Detailed outline of "trigonometry".
→ Basics - Angles
→ Basics - Triangles
→ Importance of Right Angled Triangle
→ Trigonometric Ratio (Basics)
→ Triangular Form of Trigonometric Ratios
→ Introduction to Standard Angles
→ Trigonometric Ratio of Standard Angles
→ Trigonometric Identities
→ Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles