
what you'll learn...
Overview
» An angle specifies a class of similar-right-triangles
» a side narrows down to a specific right-triangle
» Given an angle and a side "How to compute other sides?"
» Ratio of sides of similar triangles for an angle
→
→
→
» Any parameter of right-triangles (sides and angles) can be calculated using the ratios : Trigonometric Ratios
Revising
We have learned
• Many applications are mathematically modeled using the sides of right angled triangles.
• the set of similar right angled triangles are defined by an angle.
Though the set of similar right angled triangles is specified by an angle, to narrow down to a specific right angled triangle, one of the sides is specified.
A right angled triangle is specified by
• an angle - that specifies the set of similar right angled triangles
• length of one of the three sides of the triangle
When using this, it may be required to find the length of other sides of the triangle as the specified side may not be the one required in the calculations.
Specifying Right Angled Triangle: Set of similar right angled triangles are defined by one parameter: "angle". And to narrow down to one specific triangle, one side is additionally specified.
Constant Ratios
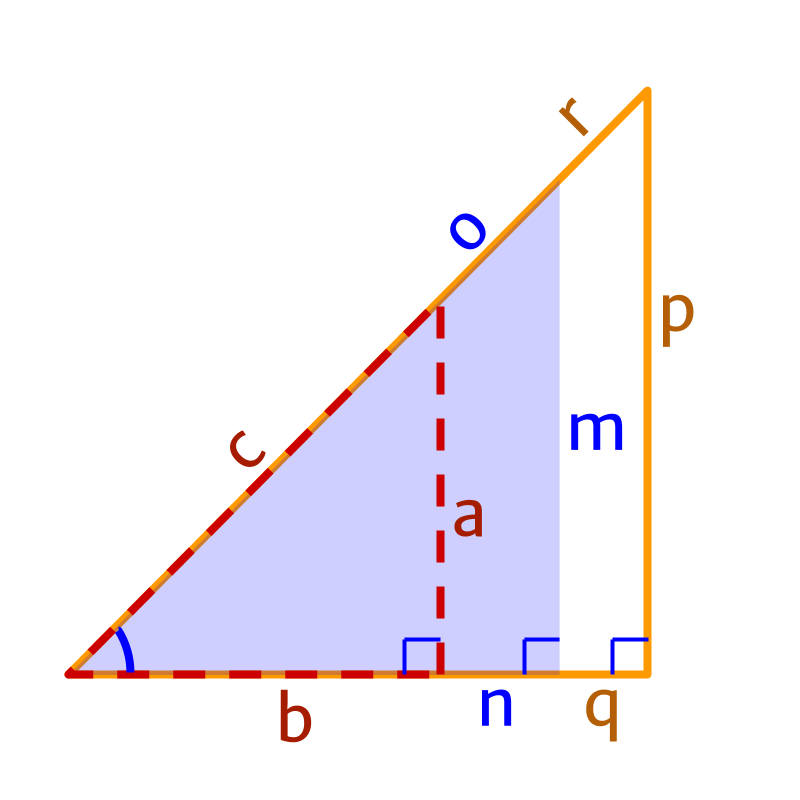
In a right angled triangle, When an angle and one of the sides is specified, what does one require to compute the other sides of the triangle?
That is, in the figure, and are given. Need to compute and .
It is noted that given one angle, the ratio of any two sides of similar triangle is a constant.
In the figure
• constant
• a different constant
• another constant
When specifying the ratio of the sides, two sides out of the three sides of the triangles are used. It can either be , or or .
To identify which sides are used in a given ratio, the sides are named with respect to the right angle and to the given angle.
The sides are called
• hypotenuse in reference to the right-angle,
• opposite side in reference to the given angle, and
• adjacent side in reference to the given angle.
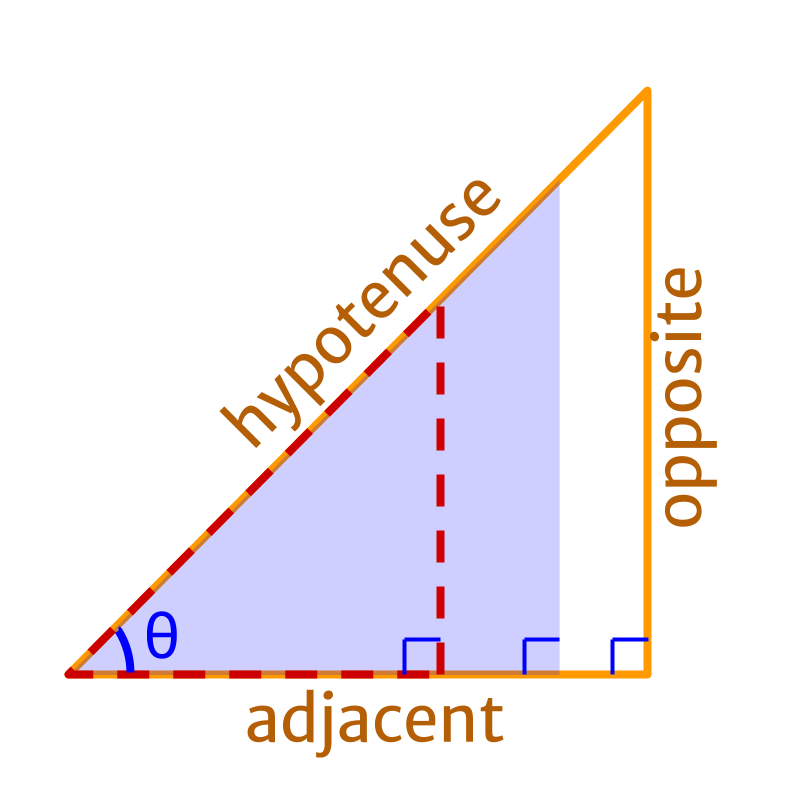
Given set of right angled triangles defined by an angle .
• position of right angle is chosen.
• the position of the given angle is chosen
• the side opposite to the right angle is fixed and called "hypotenuse"
• the side opposite to the given angle is fixed and called "opposite side"
• the side adjacent to the given angle is fixed and called "adjacent side"
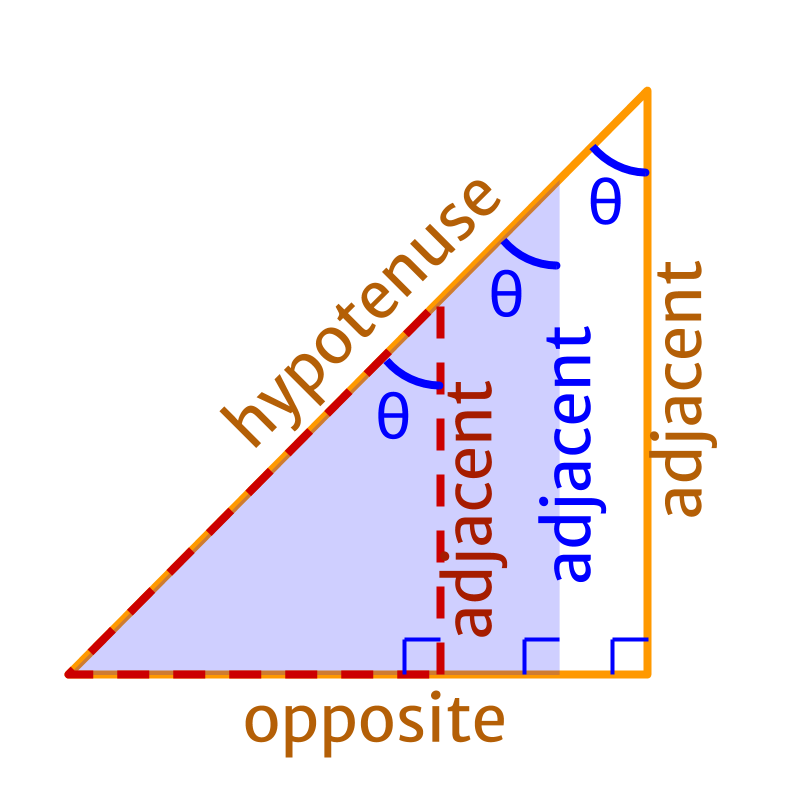
If the given angle is chosen differently...
• the side opposite to the right angle is "hypotenuse"
• the side opposite to the given angle is "opposite side"
• the side adjacent to the given angle is "adjacent side"
Trigonometric Ratios
In a right angled triangle, When an angle and one of the sides is specified, the ratio of length of sides is constant.
• Ratio between opposite side and hypotenuse is required if hypotenuse is given and opposite side is to be computed (or vise versa).
• Ratio between adjacent side and hypotenuse is required if hypotenuse is given and adjacent side is to be computed (or vise versa).
• Ratio between opposite side and adjacent side is required if opposite side is given and adjacent side is to be computed (or vice versa).
These three ratios named as .

For a set of similar right angled triangle specified by angle , the following ratios are defined. These are some of the trigonometric ratios.
Trigonometric Ratios:
In the next set of pages, why the ratios are named as , , and is explained. Pl. continue...
The word trigonometry,
Trigonometric Ratios for an angle are defined as ratio of sides of Right Angled Triangle.
Summary
Trigonometric Ratios:
Note that when is written, it does not mean four variables , , and . The same can be explained for and
is a function of variable .
Outline
The outline of material to learn "Basics of Trigonometry" is as follows.
• Detailed outline of "trigonometry".
→ Basics - Angles
→ Basics - Triangles
→ Importance of Right Angled Triangle
→ Trigonometric Ratio (Basics)
→ Triangular Form of Trigonometric Ratios
→ Introduction to Standard Angles
→ Trigonometric Ratio of Standard Angles
→ Trigonometric Identities
→ Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles