
what you'll learn...
overview
In this page, constructing rectangles is explained. It is outlined as follows.
• Properties of rectangles is explained
• The number of independent parameters in a rectangle is 11
• For a given parameter, construction of rectangles is approached as combination of triangles (sss, sas, asa, rhs, sal) and using the properties of rectangles.
understanding rectangle
A rectangle is a parallelogram with all interior angles 90∘90∘
A quadrilateral is defined by 55 parameters. A Parallelogram is defined by 33 parameters. And for a rectangle, the following properties provide additional dependency of parameters.
• all interior angles are 90∘90∘
• diagonals are equal and bisect
• opposite sides are parallel and equal
• two angles on diagonals are supplementary.
These properties cause one parameter to be dependent on other parameters and so, a rectangle is defined by 22 parameters.
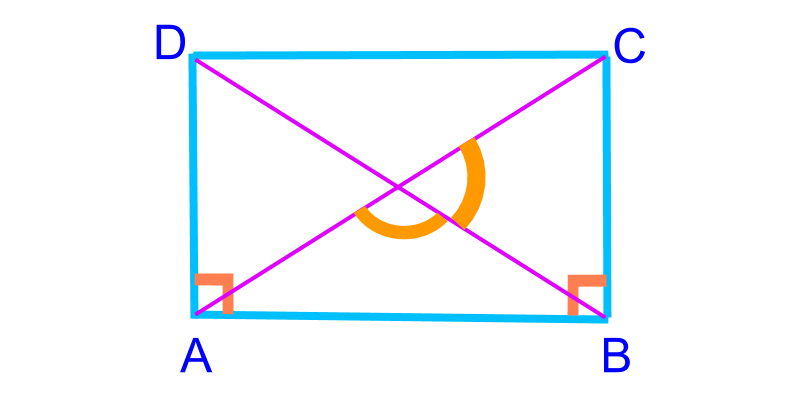
To construct a rectangle, 2 sides (¯AB, ¯BC) are given. This is illustrated in the figure. To construct, consider this as two SAS triangles ABC and ABD.
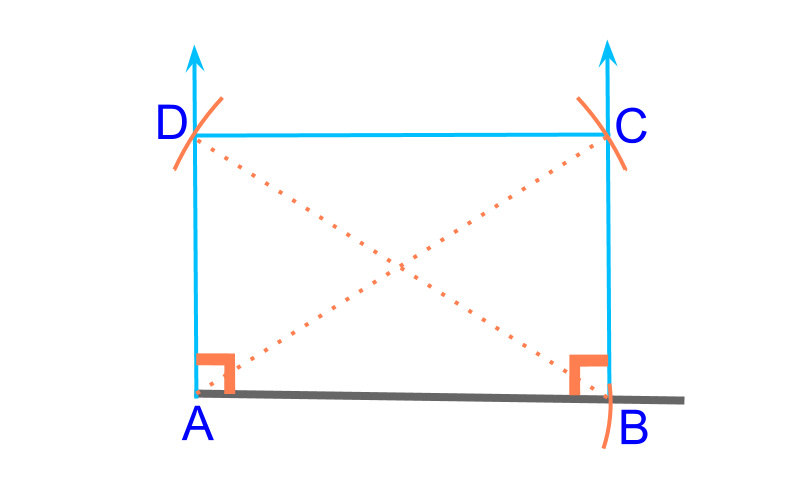
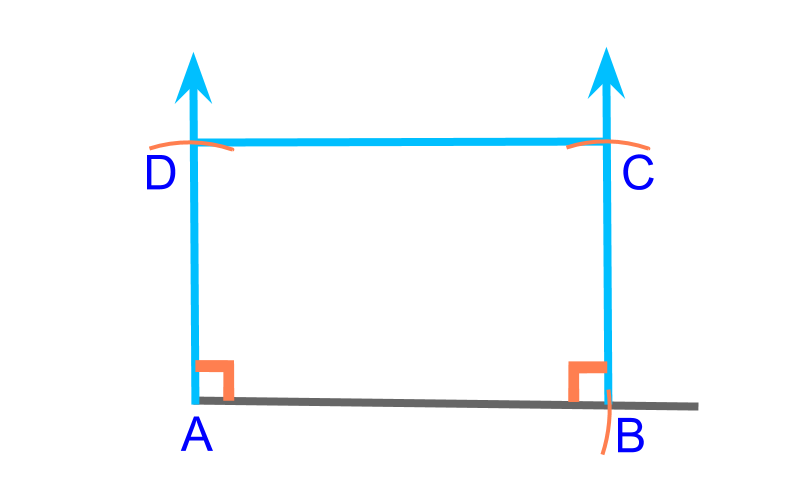
To construct a rectangle, a side (¯AB) and the diagonal (¯AC) are given. This is illustrated in the figure. To construct, consider this as two RHS triangles ABC and ABD.
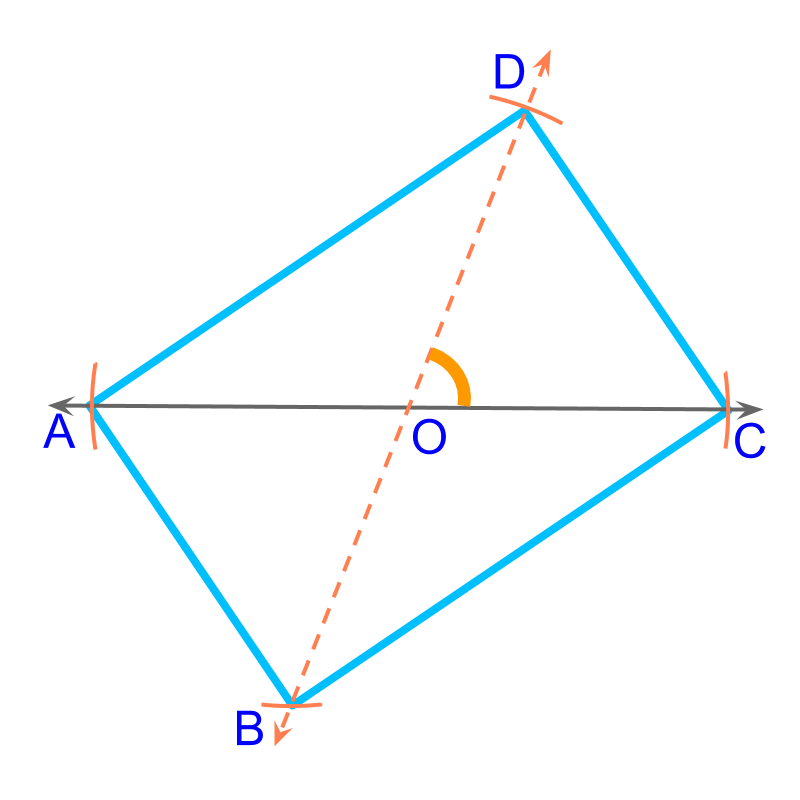
To construct a rectangle, the diagonal (¯AC) and the angle between them (∠DOC) are given. This is illustrated in the figure.
To construct the specified rectangle, "Consider this as two SAS triangle COD and AOB". Note: Use the property that diagonals bisect and mark the vertices at half diagonals.
summary

Construction of Rectangles :
Properties of rectangle
• all interior angles are 90∘
• diagonals are equal and bisect
• opposite sides are parallel and equal
The formulations of questions
• 2 sides
• 1 side and the diagonal
• the diagonal and an angle between the diagonals
use properties to figure out dependent parameters and look for triangles
Outline
The outline of material to learn "Construction / Practical Geometry at 6-8th Grade level" is as follows.
Note: click here for detailed outline of "constructions / practical geometry".
• Four Fundamenatl elements
→ Geometrical Instruments
→ Practical Geometry Fundamentals
• Basic Shapes
→ Copying Line and Circle
• Basic Consustruction
→ Construction of Perpendicular Bisector
→ Construction of Standard Angles
→ Construction of Triangles
• Quadrilateral Forms
→ Understanding Quadrilaterals
→ Construction of Quadrilaterals
→ Construction of Parallelograms
→ Construction of Rhombus
→ Construction of Trapezium
→ Construction of Kite
→ Construction of Rectangle
→ Construction of Square