
what you'll learn...
sin(A-B), cos(A+B), cos(A-B)
» Proven result
Quickly derive the identities. No need to memorize.
»
»
»
Geometrical Proof
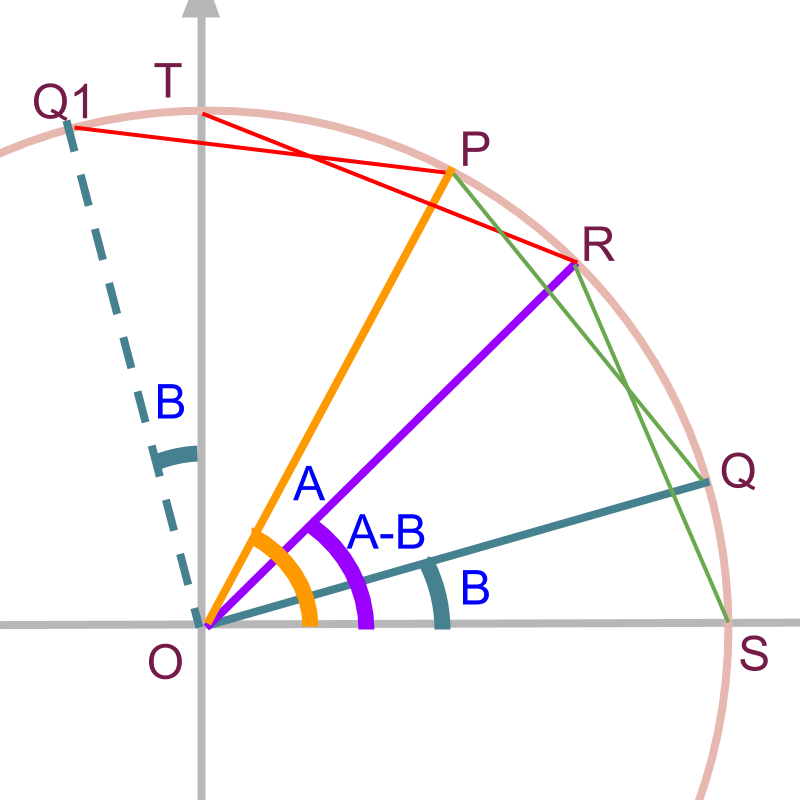 » from
» from
» from
algebraic equivalent
It was geometrically proven that . For the same result, we can work out a proof using algebra of trigonometric functions.
To calculate trigonometric values for compound angle, we will switch to using the proofs with algebra of trigonometric functions, as it is simpler. But, equivalently a geometrical proof can be worked out.
A-B
Proof for sin(A-B) and cos(A-B) using previous results and algebra of trigonometric functions.

Geometrical proof for and is outlined below.
equate square of chord lengths to derive the result given.
example
Compute .
The answer is consider as sum of standard angles and '.
summary
Outline
It is advised to do the firmfunda version of "basics of Trigonometry" course before doing this.
The outline of material to learn "Advanced Trigonometry" is as follows.
Note: go to detailed outline of Advanced Trigonometry
→ Unit Circle form of Trigonmetric Values
→ Trigonometric Values in all Quadrants
→ Trigonometric Values or any Angles : First Principles
→ Understanding Trigonometric Values in First Quadrant
→ Trigonometric Values in First Quadrant
→ Trigonometric Values of Compound Angles: Geometrical Proof
→ Trigonometric Values of Compound Angles: Algebraic Proof
→ Trigonometric Values of Compound Angles: tan cot
→ Trigonometric Values of Compound Angles: more results