
what you'll learn...
Overview
Area of a plane figure : The surface-span of a plane figure is the area of the surface. It is measured in square meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms).
 Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
surface-span
The length of a rod is the distance-span measured in meter.
For a surface of some shape (like a paper, or a leaf), the measure of the surface-span is area. Area is the surface-span of an enclosed 2D-region.
To specify distance-span or length, a reference-prototype-standard (ie a metal rod of specific material at specific temperature) was defined. Any length measurement is specified in reference to the prototype-standard.
Similarly, to specify area, a reference-prototype-standard can be defined. But, it is simpler to define the measurement of area using the already defined measure of length.

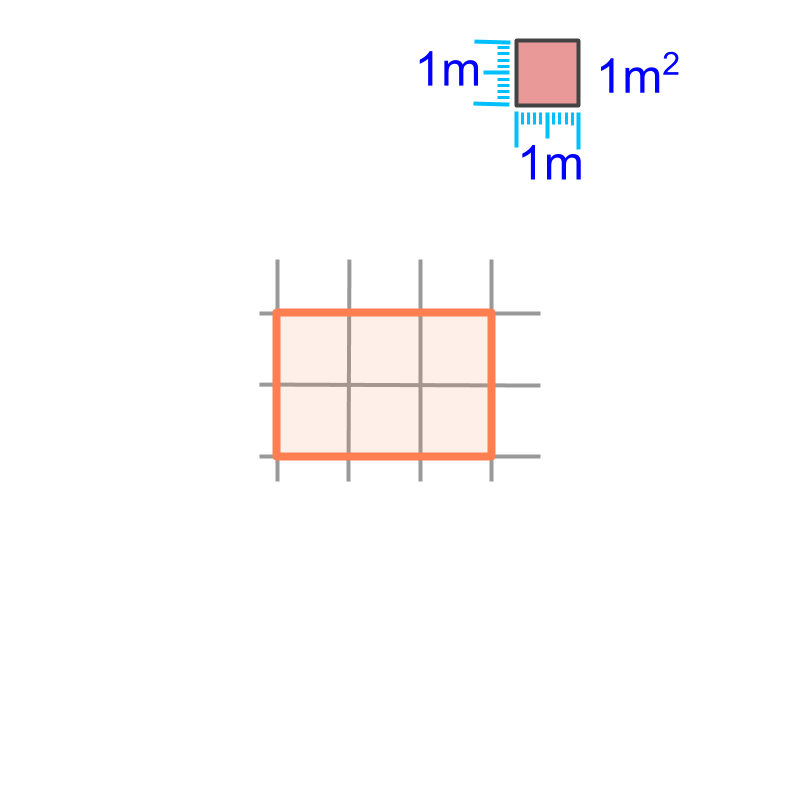
To specify the surface-span or area of a surface, a square of side meter is taken as the reference. The area of that is one square meter or . In the figure this is shown in the top right corner.
Area of a surface is given in reference to the area of a square of side meter. In the figure, the area of the given rectangle is the number of square meter squares fit in that rectangle. It is counted to , so the area of the rectangle is .
The statement "area of the paper is square meter" specifies that "The surface-span of the paper equals surface-spans of a square of side meter".
summary
Area of a plane figure : The surface-span of a plane figure is the area of the surface. It is measured in square meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms).
 Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
Outline
The outline of material to learn "Mensuration basics : Length, Area, & Volume" is as follows.
Note: click here for detailed outline of Mensuration (Basics).
• Measuring Basics
→ Introduction to Standards
→ Measuring Length
→ Accurate & Approximate Meaures
→ Measuring Area
→ Measuring Volume
→ Conversion between Units of Measure
• 2D shapes
→ Perimeter of Polygons
→ Area of Square & rectangle
→ Area of Triangle
→ Area of Polygons
→ Perimeter and area of a Circle
→ Perimeter & Area of Quadrilaterals
• 3D shapes
→ Surface Area of Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder
→ Volume of Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder