
Mensuration : Length, Area, and Volume
Welcome to the refreshingly new views to calculating perimeter, area, and volume of 2D and 3D shapes.
• Length is Distance-Span, measured in reference span of to unit long line
• Area is Surface-Span, measured in reference to span of square
• Volume is Space-Span, measured in reference to span of cube
In this basic course, the following are covered.
• Perimeter and area of simple 2D shapes
• surface area and volume of simple 3D shapes
maths > mensuration-basics > basicmensu-measuring-standard
Introduction to Standards
This topic introduces the following
• What are standard in measurement?
• What are Absolute Standards?
• What are Derived Standards?
Absolute Standards : An unit of measurement, widely accepted and used in reference to a standardized prototype.
Derived Standards : An unit of measurement that is defined using other absolute standards.
maths > mensuration-basics > basicmensu-measuring-length
Introduction to Measuring Length
This topic introduced measuring length as "distance-span". It is an absolute standard and measured in reference to a standard unit.
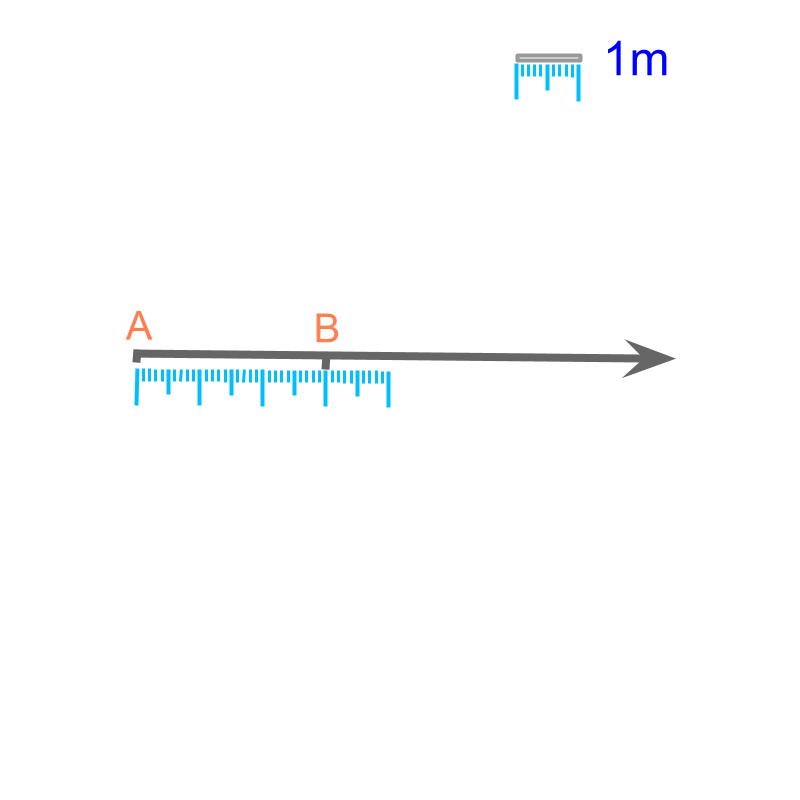 Length : The distance-span between two points is the length. It is measured in meter or in one of its other forms. Length is specified as a number in reference to the reference-prototype-standard meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms).
Length : The distance-span between two points is the length. It is measured in meter or in one of its other forms. Length is specified as a number in reference to the reference-prototype-standard meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms).
maths > mensuration-basics > measuring-length-approximation
Accurate measure and Approximate measure
In this topic accuracy of measurement is explained.
Accuracy of Measurements : Measurement can be performed to a desired accuracy level.
When the accuracy is specified to a lower level, the measurement is approximate measurement.
maths > mensuration-basics > basicmensu-measuring-area
Introduction to Measuring Area
This topic introduced measuring area as "surface-span". It is a derived standard and measured in reference to a standard square.
Area of a plane figure : The surface-span of a plane figure is the area of the surface. It is measured in square meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms).
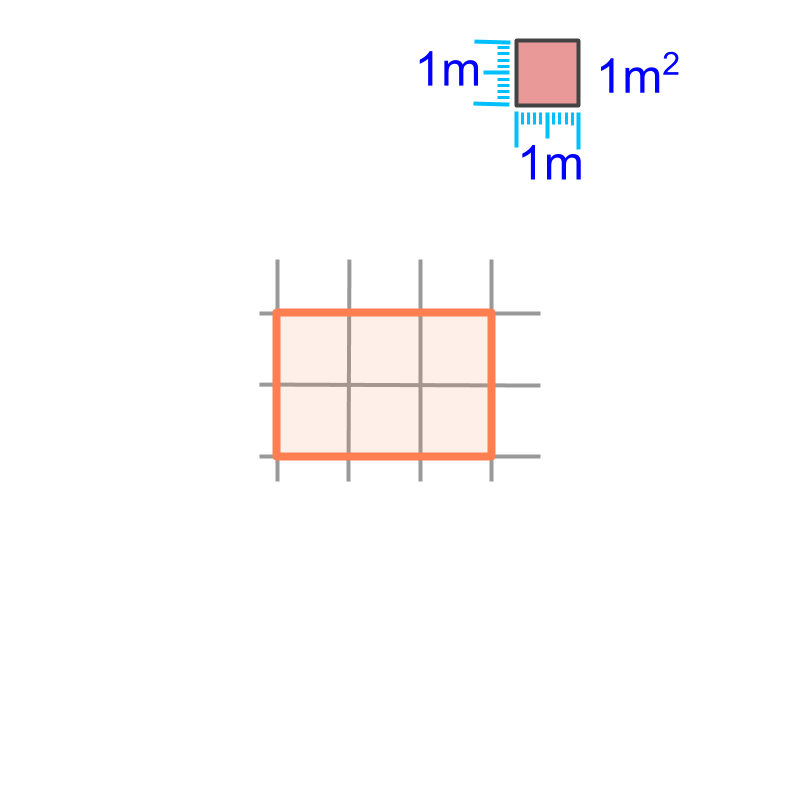 Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
Area is specified as a number in reference to the surface-span of a square of meter side.
maths > mensuration-basics > basicmensu-measuring-volume
Introduction to Measuring Volume
This topic introduced measuring volume as "space-span". It is a derived standard and measured in reference to a standard cube.
Volume of a solid : The space-span of a solid is the volume of the solid. It is measured in cubic meter (or in one of other derived or similar forms.)
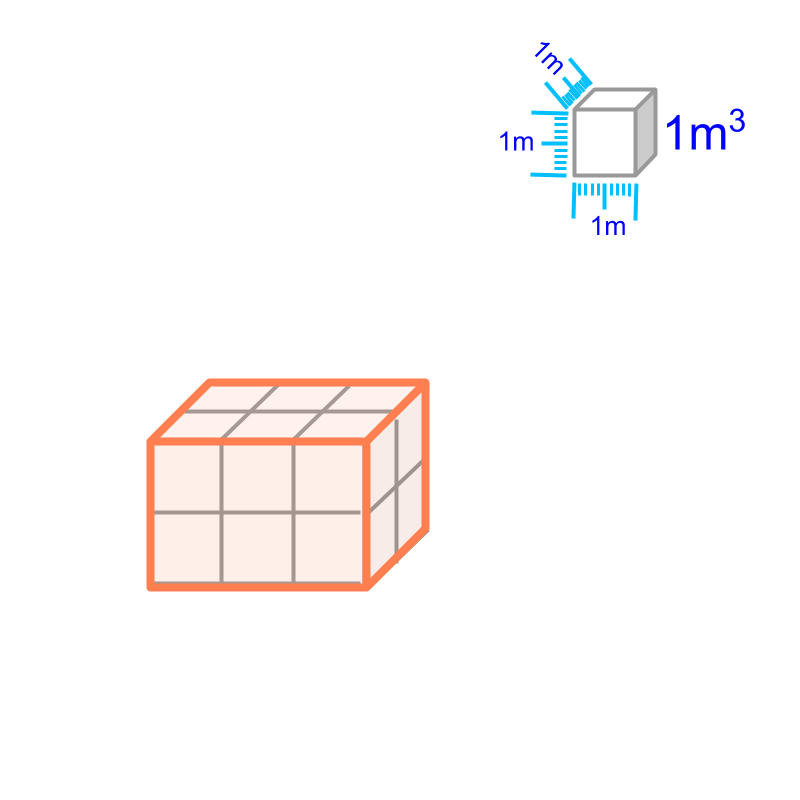 Volume is specified as a number in reference to the space-span of a cube of meter side.
Volume is specified as a number in reference to the space-span of a cube of meter side.
maths > mensuration-basics > basicmensu-units-conversion
Conversion of Units of Measure
This topic provides a very brief overview of conversion of Units of Measure.
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-perimeter-polygons
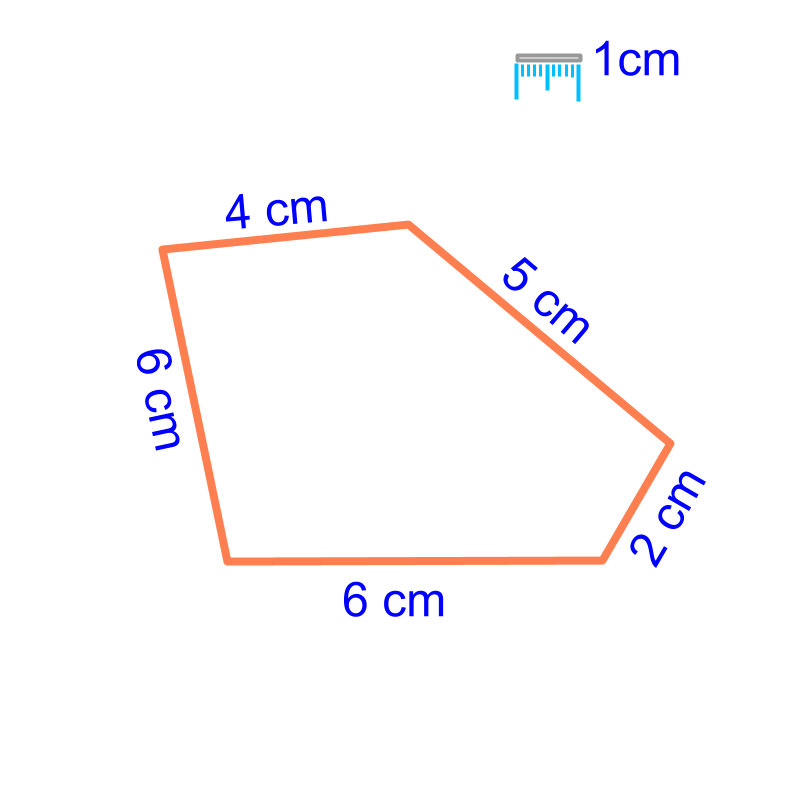
Perimeter: Square, Rectangle, Triangle, Polygons
Finding perimeter of simple figures (squares, rectangle, triangle, polygon) are revised.
Perimeter :
Perimeter of a figure is the length of the line or curve forming the boundary of the figure.
Perimeter of square
Perimeter of rectangle
Perimeter of triangle
Perimeter of polygon
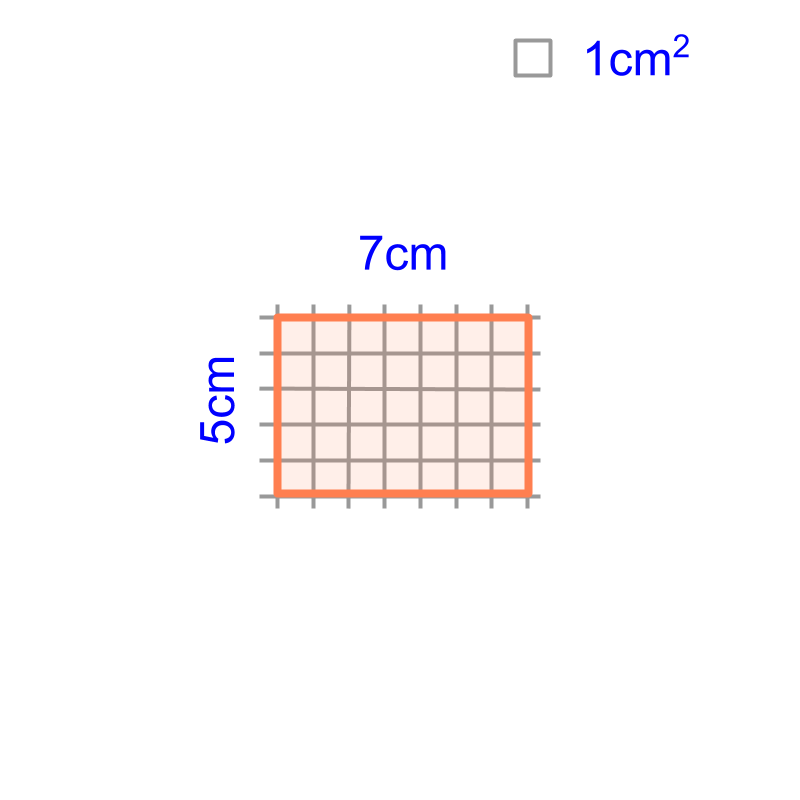
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-area-square-rectangle
Area of Square and Rectangle
Area of a Square and a Rectangle :
Area of square
Area of rectangle
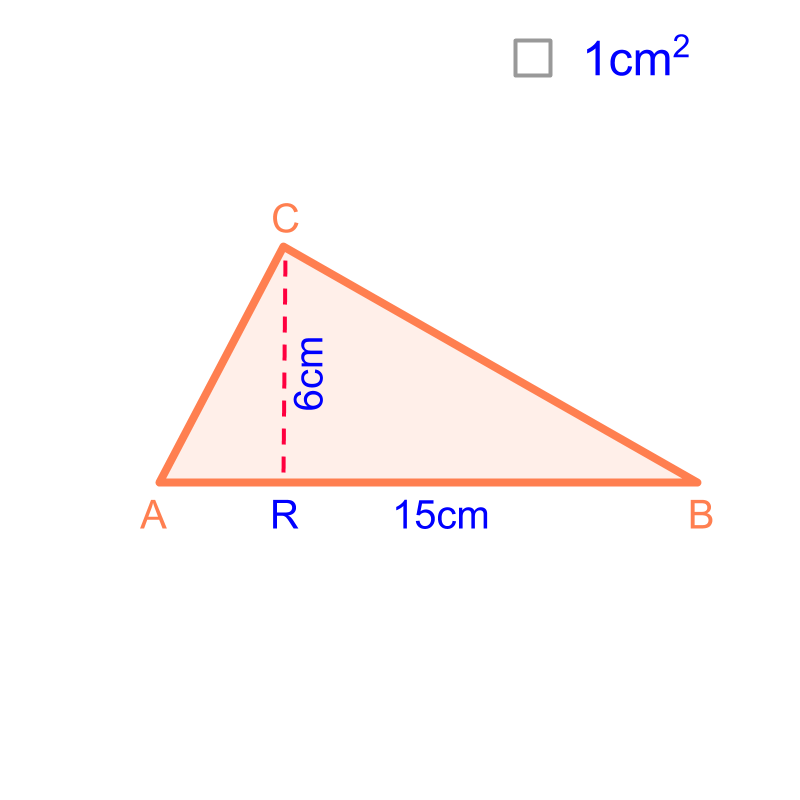
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-area-triangle
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated based on geometrical properties. In this chapter, the different configurations of triangles are illustrated and a common formula is derived.
Area of a Triangle:
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-area-polygons
Area of Polygons
Area of a Polygon : Consider a polygon to be combination of known geometrical forms, mostly triangles.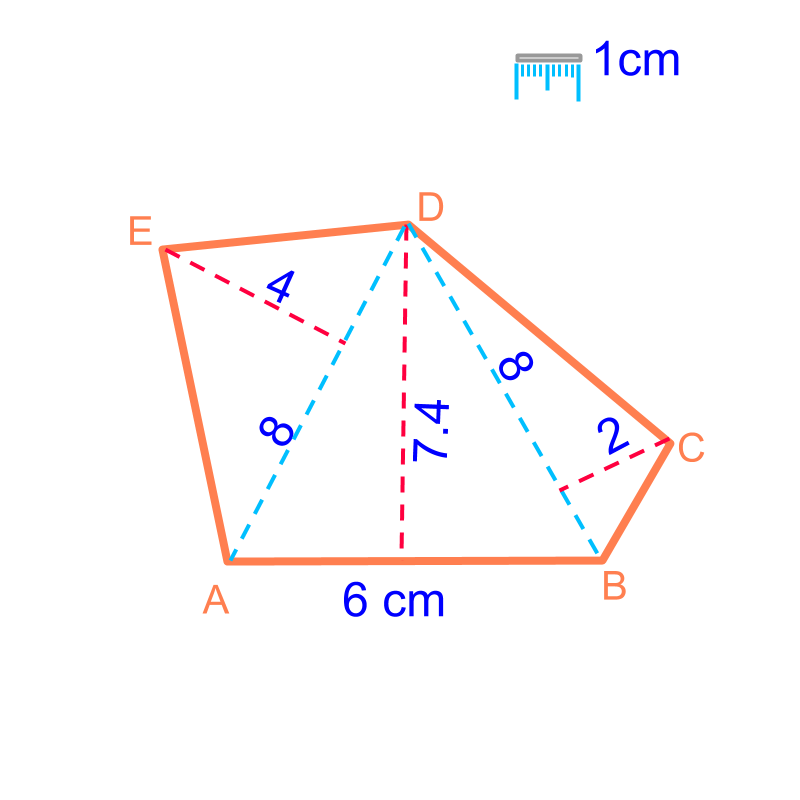 The geometrical forms and the formula for area are:
The geometrical forms and the formula for area are:
Area of a triangle
Area of a trapezium
Area of a parallelogram
Area of a kite
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-perimeter-area-circle
Circumference and Area of a Circle
In this page, the formula to find circumference of a circle is introduced.
Circumference of a Circle: :
Circumference and
is the radius of the circle
is the diameter of the circle
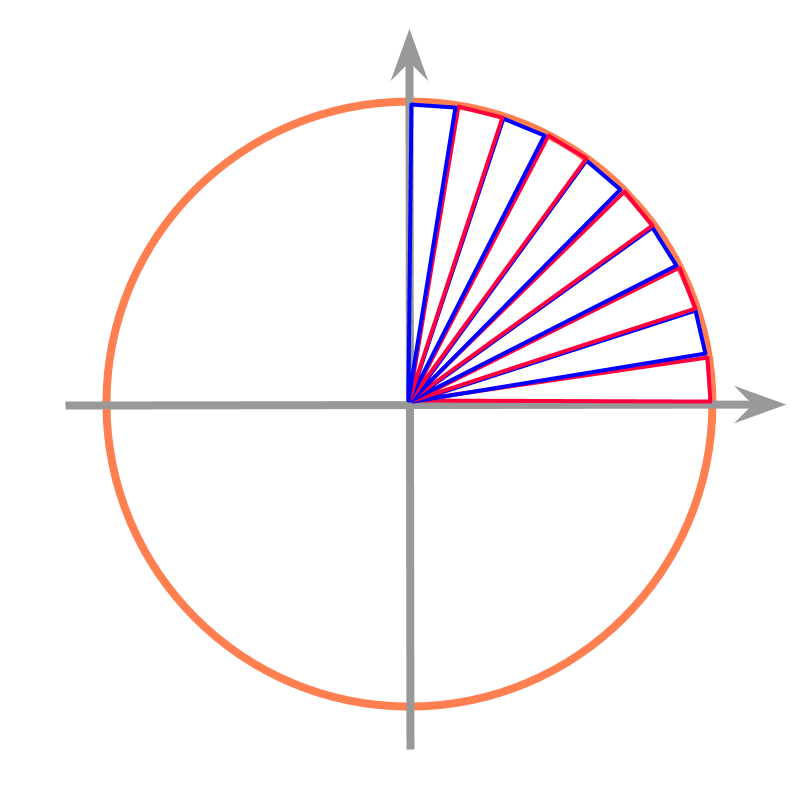 Area of a Circle :
Area of a Circle :
is the radius of the circle
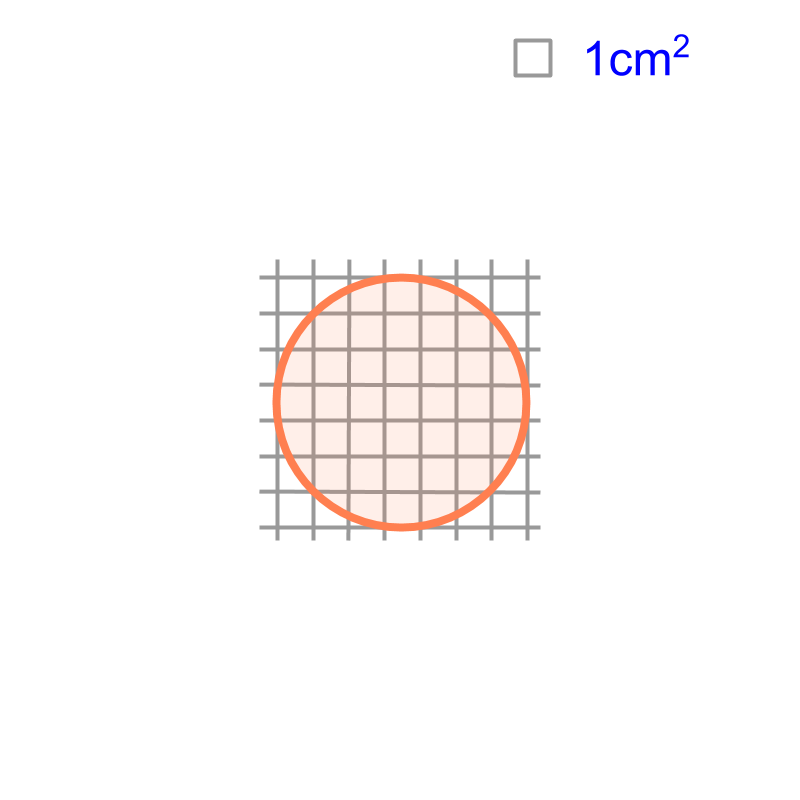
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-mensuration-quadrilaterals
Perimeter and Area of Various Quadrilaterals
In this page, the formula to find area of various quadrilaterals is introduced.
Area of Some Quadrilaterals : Consider the polygon shapes as combination of triangles and find sum of area of the triangles.
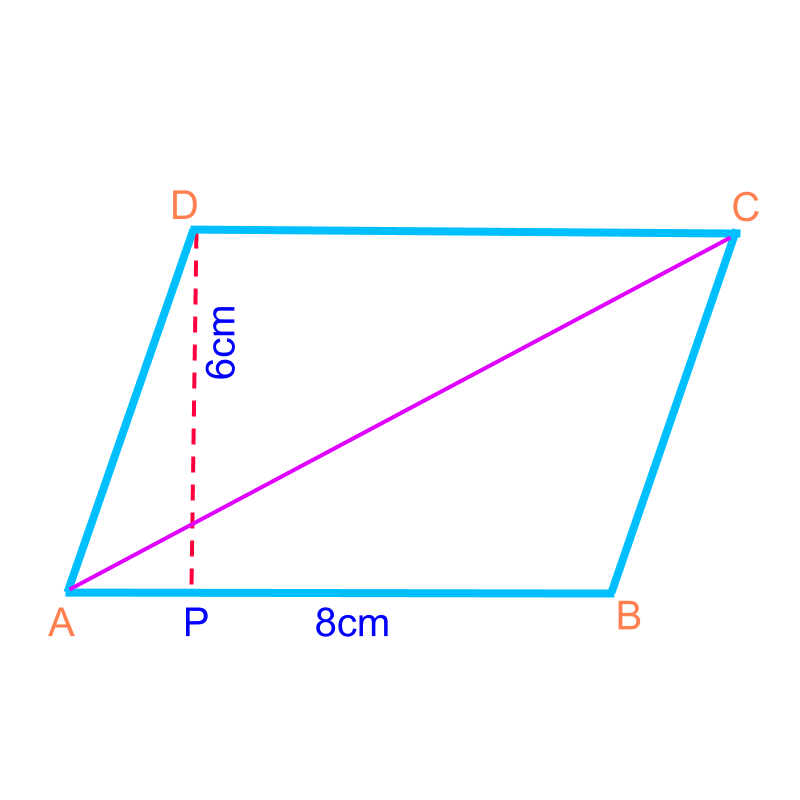
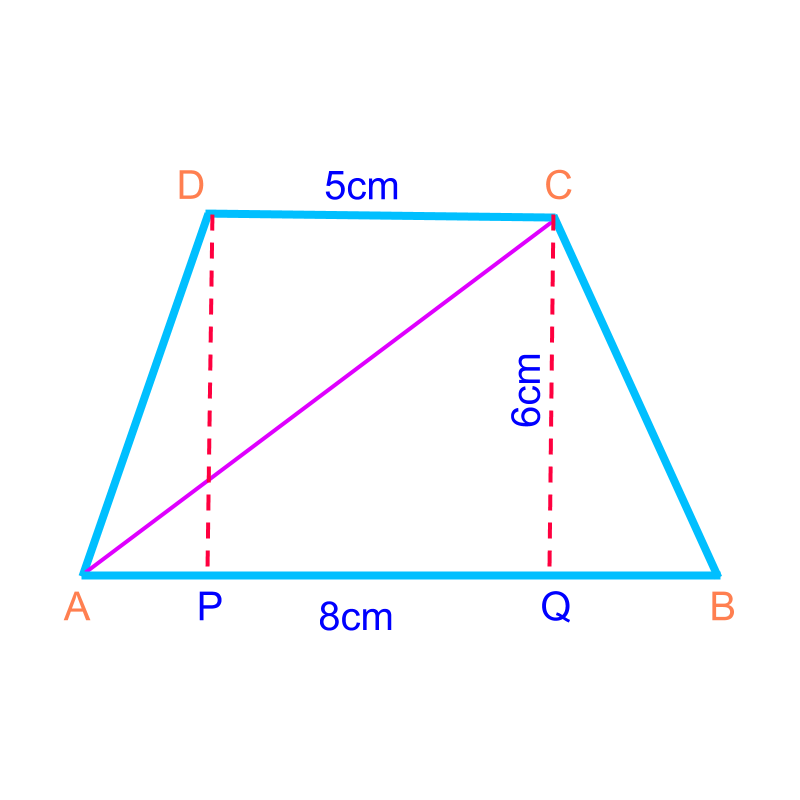
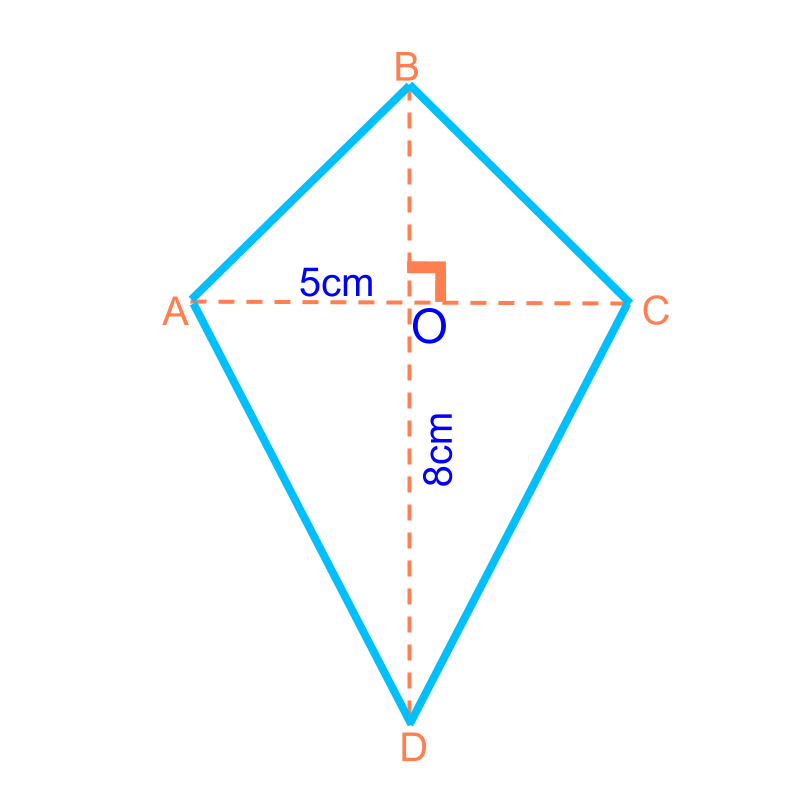
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-surface-area-basic-shapes
Surface Area of Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder
In this page, Finding surface area of simple figures (cube, cuboid, and cylinder) are revised without much discussion.
Surface Area of Some Shapes:
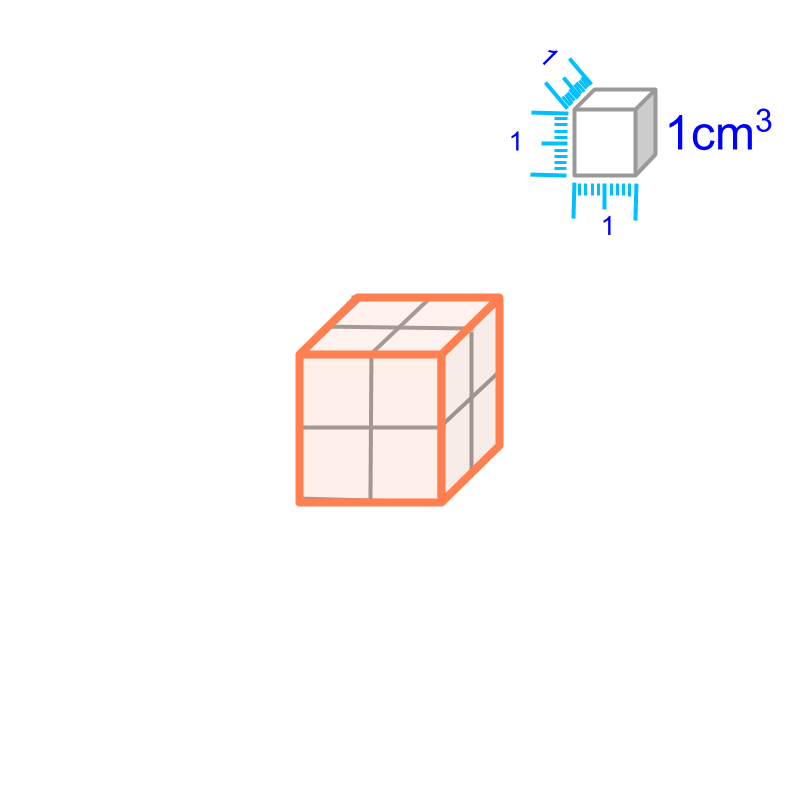 Surface Area of cube
Surface Area of cube
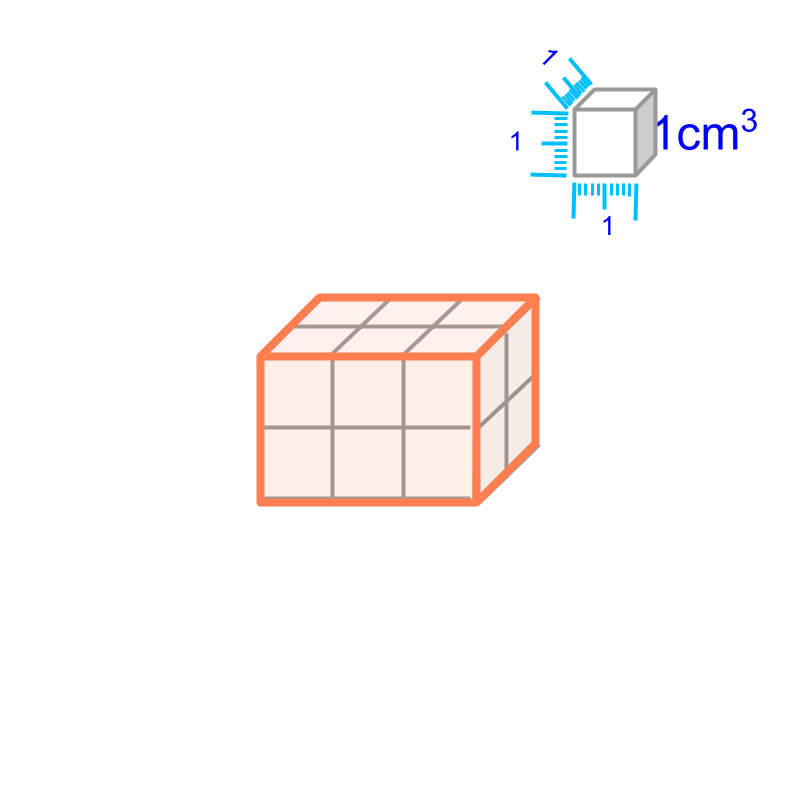 Surface Area of cuboid
Surface Area of cuboid
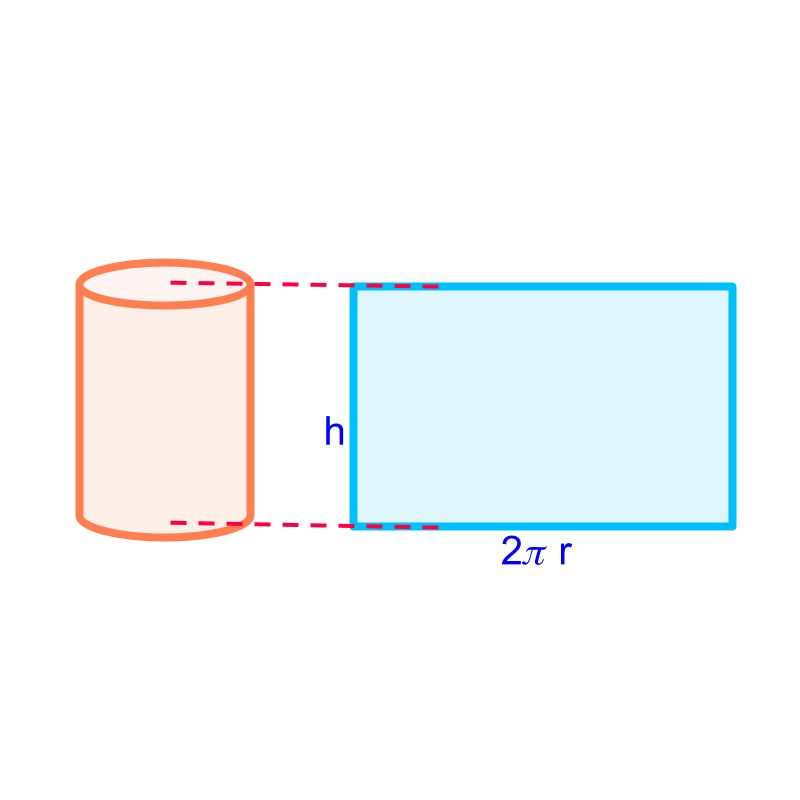 Curved Surface Area of Cylinder
Curved Surface Area of Cylinder
Surface Area of cylinder
maths > mensuration-basics > basic-volume-basic-shapes
Volume : Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder
In this page, Finding volume of simple figures (cube, cuboid, and cylinder) are revised without much discussion.
Volume of Some Solids :
 Volume of cube
Volume of cube
 Volume of cuboid
Volume of cuboid
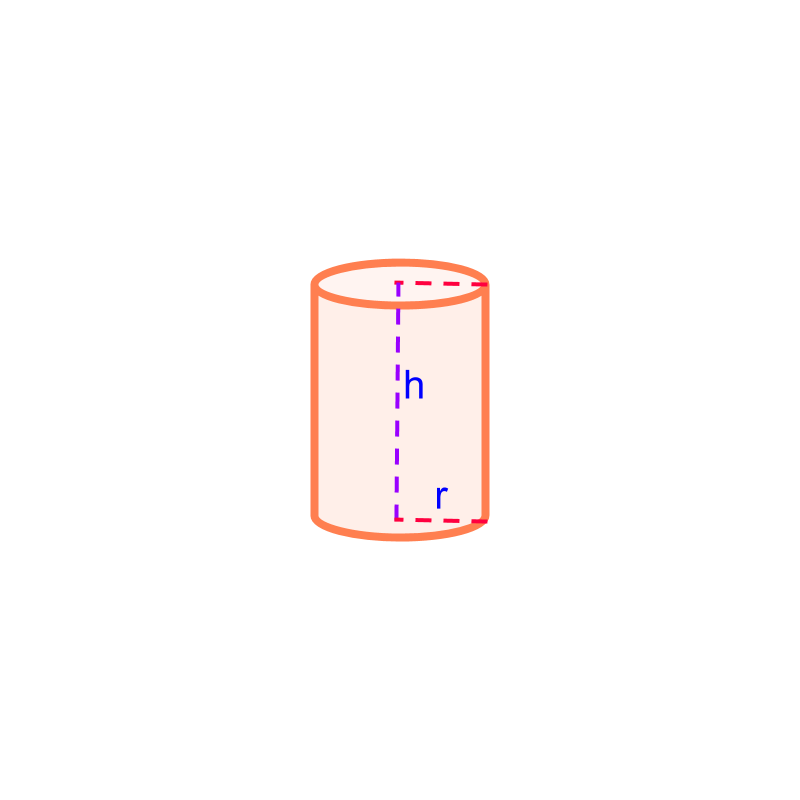 Volume of cylinder
Volume of cylinder