
what you'll learn...
Overview
Area of a Triangle:
type 1
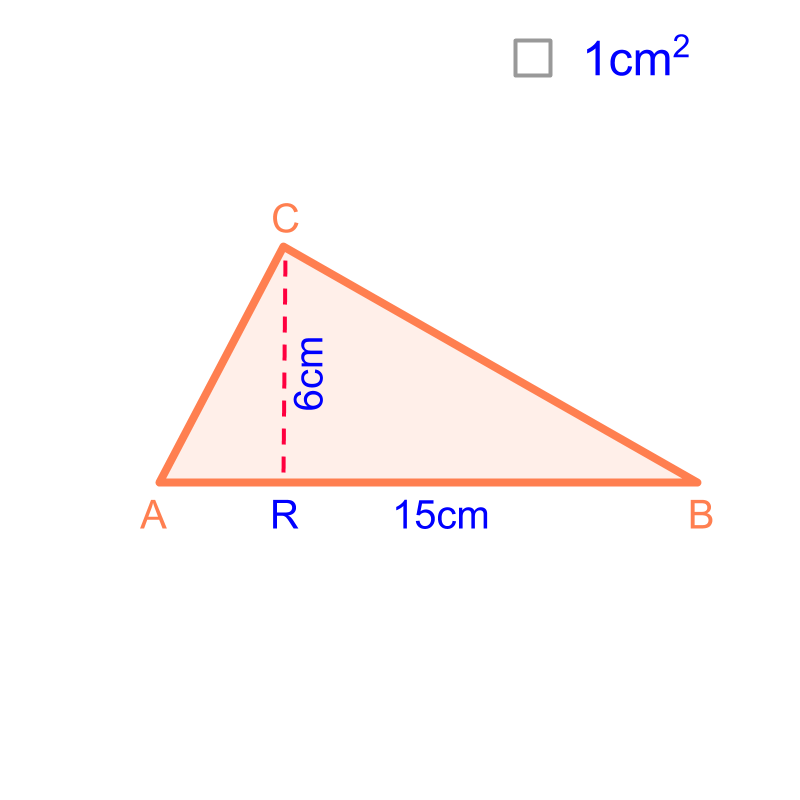
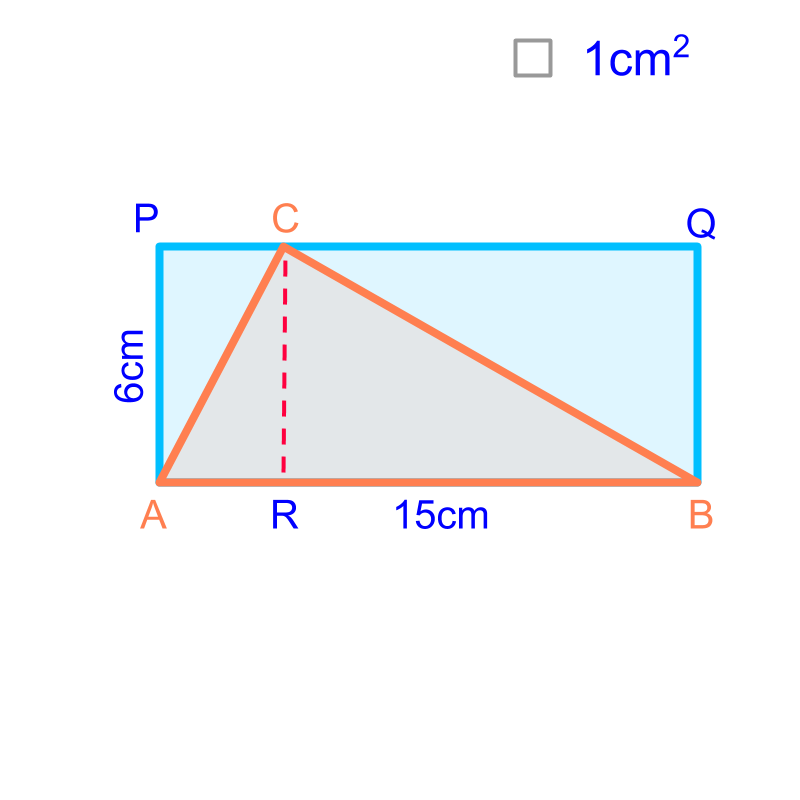
Consider the triangle given in the figure. The base is cm and height is cm. To find the area of the triangle, compare the triangle with a rectangle of cm by cm.
The triangle of base cm and height cm is placed over a rectangle of length cm and width cm. It is noted that the triangle splits the rectangle into equal halves. The area of the triangle is half of the area of rectangle OR in other words,
type 2

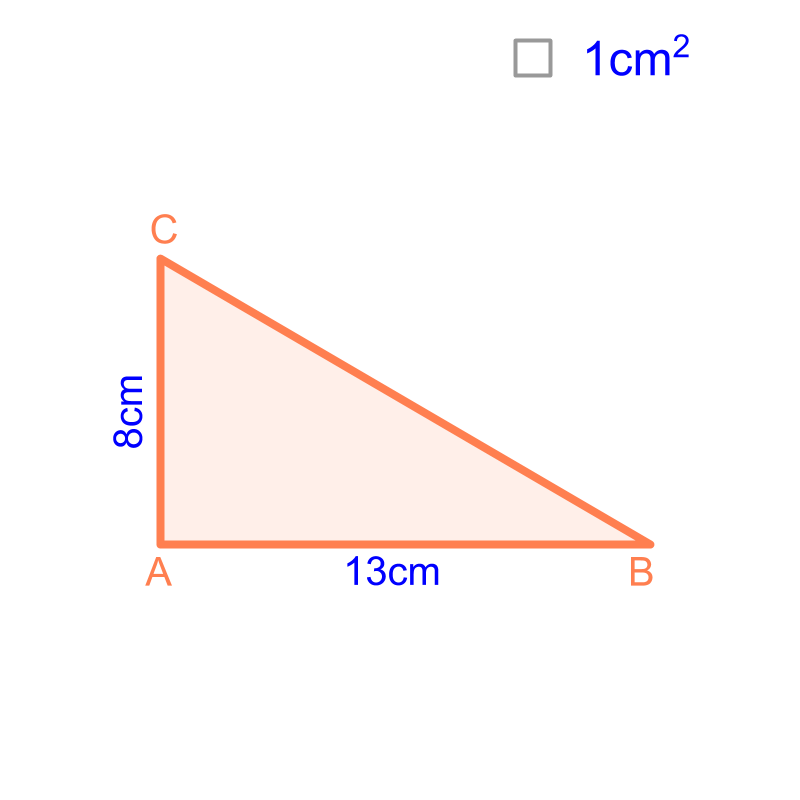
Consider the triangle given in the figure. The base is cm and height is cm. To calculate the area, compare the triangle with a rectangle of cm by cm.
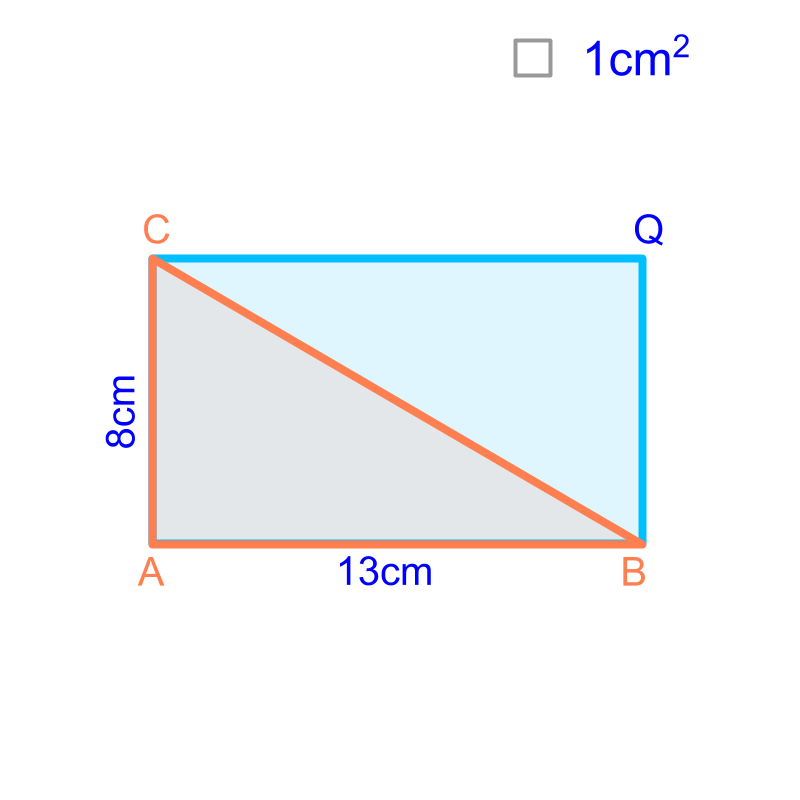
The triangle of base cm and height cm is placed over a rectangle of length cm and width cm.
The rectangle is visualized into two parts and
The triangle is visualized into two parts and
It is noted that the area of the triangle is half of the rectangle and area of the triangle is half of the rectangle .
The area of the triangle is sum of area of the two triangles and .
half the area of rectangles and .
The area of the triangle is half of the area of rectangle OR in other words,
type 3
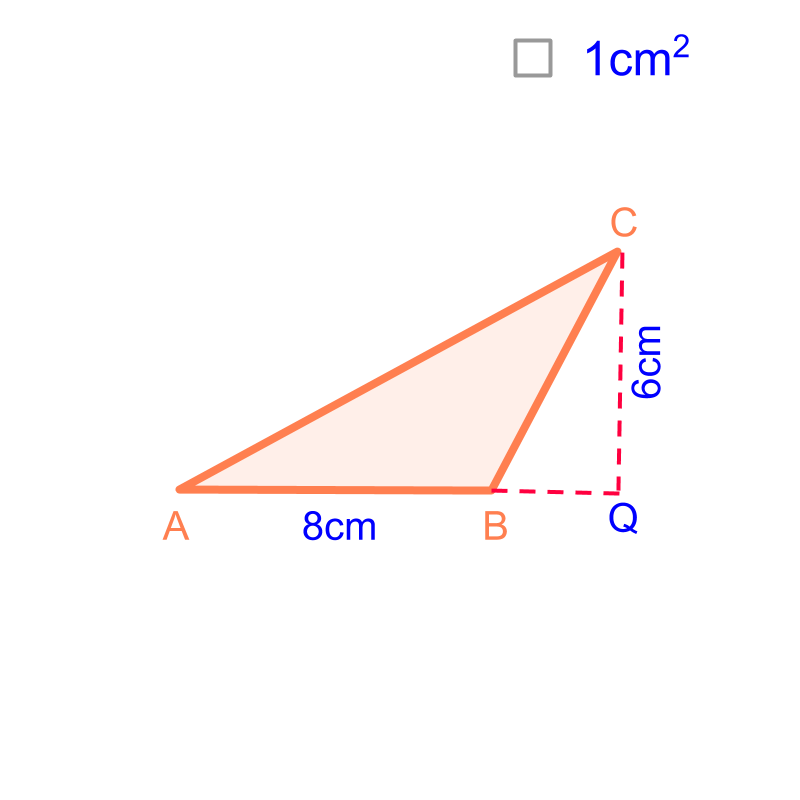
Consider the triangle given in the figure. The base is cm and height is cm. To calculate the area, compare the triangle with a rectangle covering
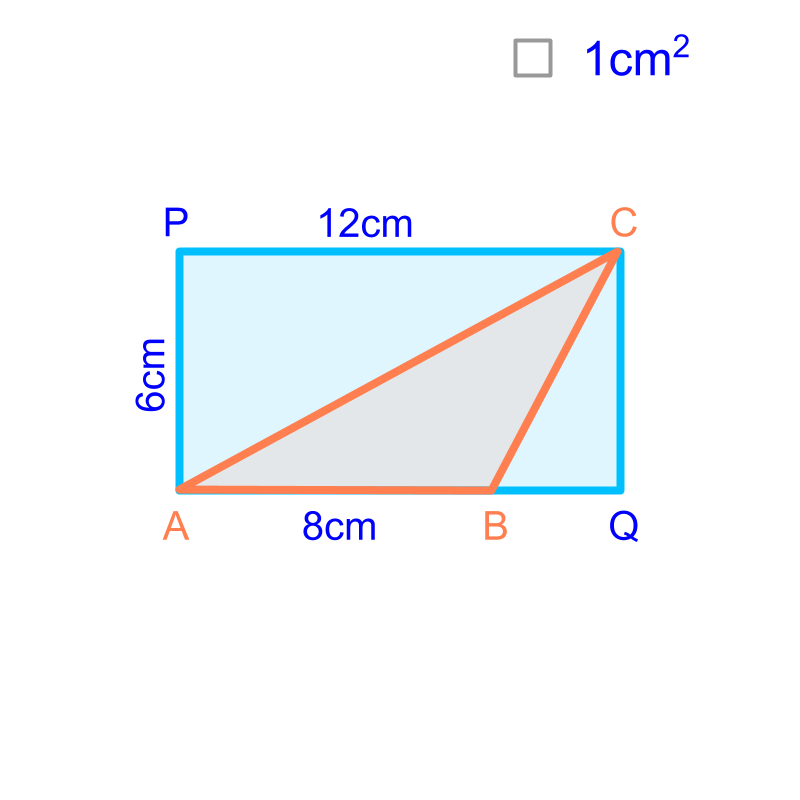
The triangle of base cm and height cm is placed over a rectangle . The rectangle is visualized to two triangles and .
The area of triangle is half of the rectangle.
The area of the triangle is
area of area of
The area of the triangle is half of the area of rectangle OR in other words,
common formula
Consider the three types of triangles,



For all the types, the area is derived as
What is the area of the triangle with base cm and height cm?
The answer is ""
summary
Area of a Triangle:

Outline
The outline of material to learn "Mensuration basics : Length, Area, & Volume" is as follows.
Note: click here for detailed outline of Mensuration (Basics).
• Measuring Basics
→ Introduction to Standards
→ Measuring Length
→ Accurate & Approximate Meaures
→ Measuring Area
→ Measuring Volume
→ Conversion between Units of Measure
• 2D shapes
→ Perimeter of Polygons
→ Area of Square & rectangle
→ Area of Triangle
→ Area of Polygons
→ Perimeter and area of a Circle
→ Perimeter & Area of Quadrilaterals
• 3D shapes
→ Surface Area of Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder
→ Volume of Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder