
what you'll learn...
overview
On measuring a real-life object, it is found that a number can have decimal digits that do not repeat and do not end. Such decimal numbers -- with decimal digits that do not repeat and do not terminate -- are called "irrational numbers".
numbers in practice
Consider length of a pencil. One of the ways to measure the length of a pencil, is to mark the ends of the pencil into a line-segment and measure the length of the line-segment. This essentially measures the "distance-span between the two ends of the pencil".
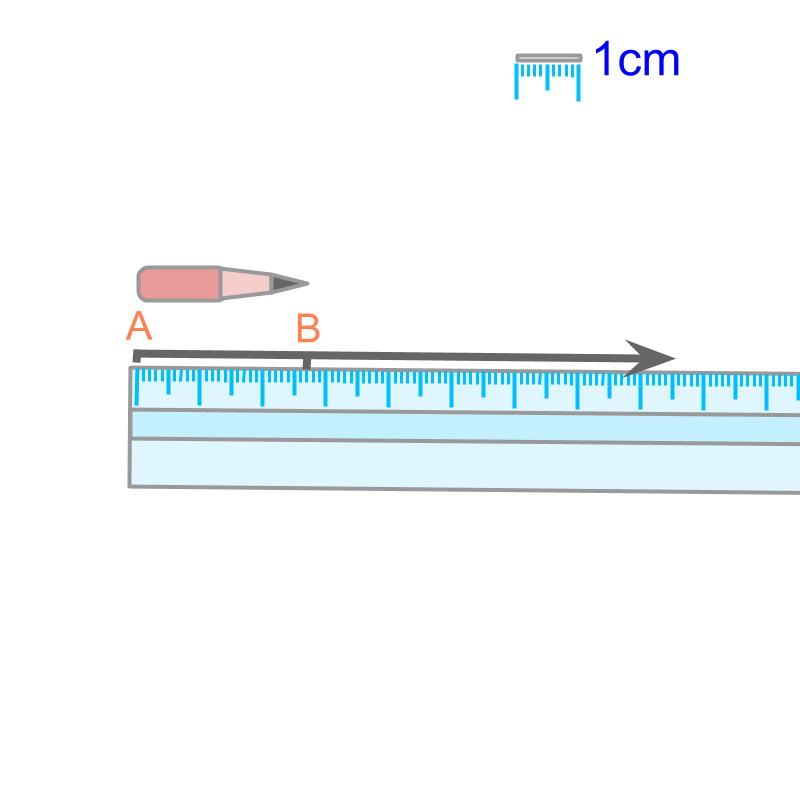
To measure the length of a pencil, an equivalent line segment is taken. The line segment and the graduated scale are shown in the figure. Note the legend on the right-top of the figure showing centimeter. What is the length of the line segment ?
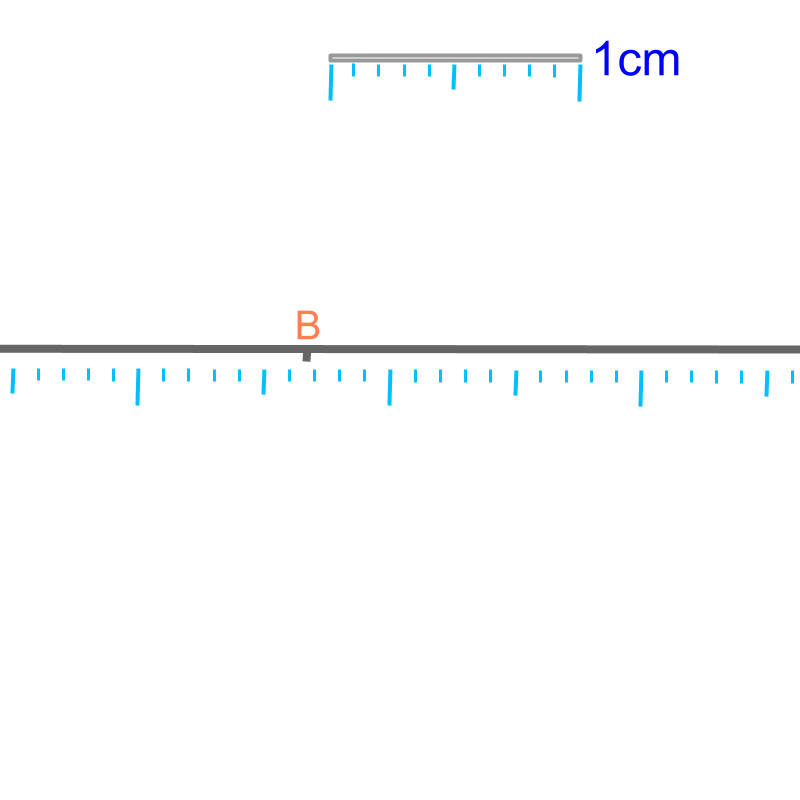
The figure is magnified. Note the legend showing the modified length. The point is not shown. "the length of is approximately "
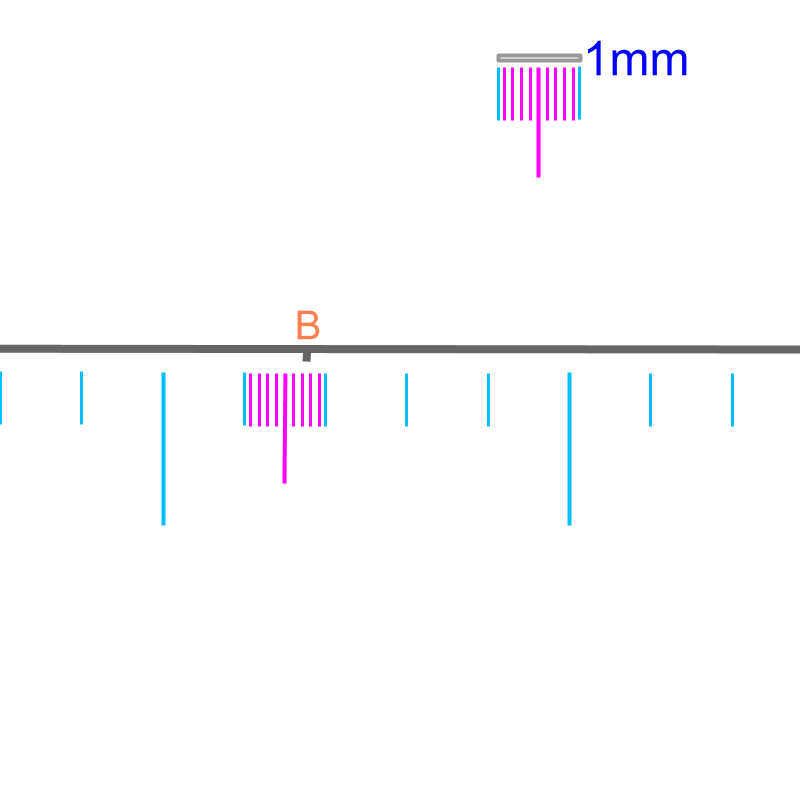
The figure is magnified even larger. Note the legend showing the modified length. The length of is better approximated to
at what accuracy?

The line-segment can be measured at different accuracies.
• The length is when measured with a graduated-scale.
• The length is when magnified and measured with a better instrument than a scale.
• The length is when measured at much higher accuracy.
For most practical applications, the length of is good enough.
Note 1: The line represents a real object. It can be a leaf, or a rod. The important point being, the measurements in real-life are approximated.
Note 2: The length of a real object can be exactly measured too. For example, a pencil of length exactly cm is possible. That object, when magnified and measured with high accuracy, will be of length cm only.
Note 3: The length of a real object can be a decimal number, that does not end or does not repeat. For example, a pencil is of length cm length. The decimals in the number does not end or repeat. It is an interesting observation, that will help to understand some concepts later.
The word "accuracy" means: state of being exactly correct.
defining
On measuring a real-life object, it is found that a number can have decimal digits that do not repeat and do not end. Such decimal numbers -- with decimal digits that do not repeat and do not terminate -- are called "irrational numbers".
The word "irrational" means: that cannot be given as a ratio.
Irrational Numbers : Decimal numbers that has decimal digits that do not end and do not have a pattern of digits that repeats. eg: accurate length of a pencil is .
advanced concepts
advanced concepts (not for regular readers)
There are two types of decimal numbers with decimal digits that do not end and do not have a pattern that repeats.
• Algebraic irrational numbers: Irrational numbers that are solutions to algebraic equations. eg: The square root of which is a solution to .
• Transcendental irrational numbers: Numbers that are not solutions to algebraic equations. The ratio of circumference to diameter of a circle is an irrational numbers. The diameter is chosen to be in the given standard cm. Circle is a regular curve and the length of the curve is measured accurately and found to be an irrational number.
In transcendental irrational numbers, the following is included.
Accurate measurement of real-life object in a unrelated standard.
eg: pound is approximated to grams. Pound is a standard defined based on mass of grains (wheat or barley). Kilogram is a standard defined based on mass of liter water at the temperature of melting point. This irrational number is similar to the example illustrated above -- accurately measuring a real-life object.
Similarly, curve-length of a circle is a measurement in an unrelated standard and so is a irrational number.
summary
Irrational Numbers : Decimal numbers that has decimal digits that do not end and do not have a pattern of digits that repeats.
eg: accurate length of a pencil is .
Outline
The outline of material to learn "decimals" is as follows.
Note: goto detailed outline of Decimals
• Decimals - Introduction
→ Decimals as Standard form of Fractions
→ Expanded form of Decimals
• Decimals - Conversion
→ Conversion between decimals and fractions
→ Repeating decimals
→ Irrational Numbers
• Decimals - Arithmetics
→ Comparing decimals
→ Addition & Subtraction
→ Multiplication
→ Division
• Decimals - Expressions
→ Expression Simplification
→ PEMA / BOMA