
what you'll learn...
overview
Decimals are fractions with standard place values. In this page, the following for decimals are explained.
• multiplication in first principles -- repeatedly combining a quantity and measuring the combined and
• simplified procedure : Sign property of multiplication and Multiplication by Place value for Decimals.
decimal repeated addition
Multiplication can be understood as "multiplicand repeated multiplier number of times".
Decimals are fractions with standardized place-values.
Consider .
By first principles, the multiplicand is repeated multiplier number of times.
This is done in two steps,
first step: repeated (denominator of ) times is .
Second step: the result from the first step is repeated (numerator of ) times is
The product is , or equals in decimals.
aligned or opposed to direction
Decimals are directed numbers, that is decimals are either positive or negative.
aligned in direction is "".
opposed in direction is "".
Directed numbers, positive and negative, are explained as "aligned in direction" and "opposed in direction" respectively.
Consider .
By first principles, the multiplier aligned in direction is repeated multiplier opposed in direction number of times.
This is done in two steps,
first step: repeated (denominator of ) times is .
Second step: the result from the first step is repeated (numerator of ) timesopposed in direction is opposed in direction.
The product is opposed in direction, or equals in decimals.
Decimal multiplication by first principles : Decimal multiplication is repeating the multiplicand, multiplier number of times with sign of the numbers (direction) handled appropriately.
simplifications recap
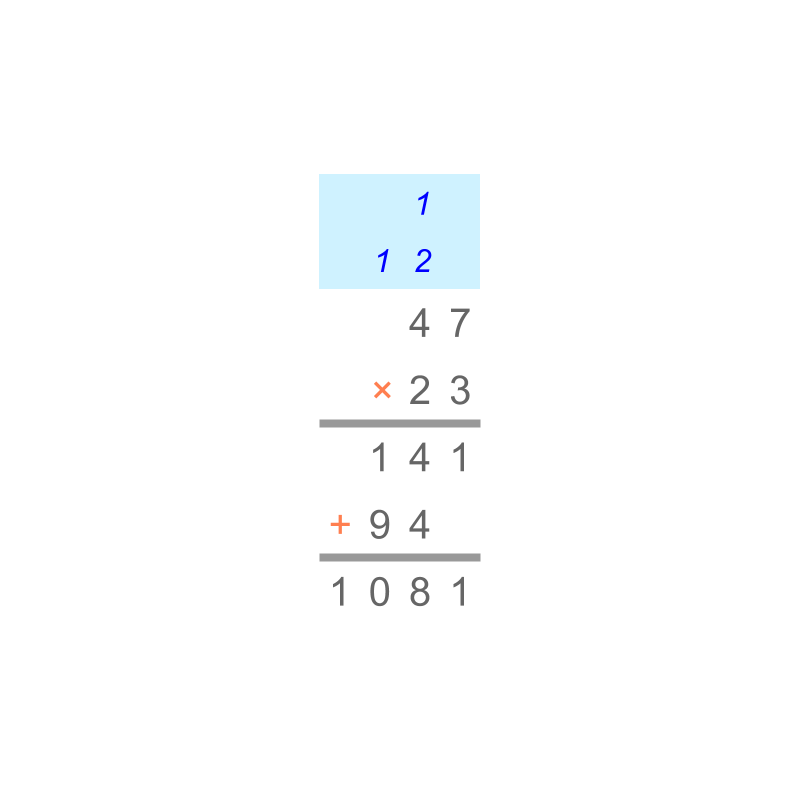
In whole numbers, we have studied Multiplication by Place-value as illustrated in the figure. This procedure is used in decimals in a later step.
In Integers, we have studied Sign-property of Multiplication.
+ve +ve = +ve
+ve -ve = -ve
-ve +ve = -ve
-ve -ve = +ve
This is applicable to decimals.
In Fractions, we have studied Multiplication of Numerators and Denominators.
For example, to multiply , the numerators are multiplied and denominators are multiplied. The product is .
Similarly decimals are multiplied keeping in mind the place-value representation.
For example, to multiply , it is equivalently thought as and so the product is . Note that is multiplied as per "multiplication by place-value".
simplify decimal multiplication
Consider multiplication of
This is equivalently
Understanding the above, a simplified procedure to multiply the decimals is devised.
The decimal point of multiplicand and multiplier are removed and the numbers are multiplied as integers.
eg: is modified to the integer form .
is modified to the integer form .
The number of decimal-places in the multiplicand and multiplier are counted.
eg: has decimal-places.
has decimal-places.
Now the integer forms are multiplied.
eg:
The number of decimal places of multiplicand and multiplier are added.
eg: .
The product of integer forms is modified to have the number of decimal points give by the sum above.
eg: is modified to which has decimal points.
example
What is
The answer is "".
Total number of decimal places in the multiplicand and multiplier is
So the product decimal place moves places
summary
Decimal Multiplication -- Simplified Procedure :
The signs (+ve / -ve) are handled as in Sign-property of Integer Multiplication
• +ve +ve = +ve
• +ve -ve = -ve
• -ve +ve = -ve
• -ve -ve = +ve
The decimal places are removed and the multiplication is carried out as per Whole number Multiplication by Place Value.
• The decimal place is re-introduced in to the product.
• The decimal-point is moved to the left -- a number of digits equal to the total number of decimals in multiplier and multiplicand
Outline
The outline of material to learn "decimals" is as follows.
Note: goto detailed outline of Decimals
• Decimals - Introduction
→ Decimals as Standard form of Fractions
→ Expanded form of Decimals
• Decimals - Conversion
→ Conversion between decimals and fractions
→ Repeating decimals
→ Irrational Numbers
• Decimals - Arithmetics
→ Comparing decimals
→ Addition & Subtraction
→ Multiplication
→ Division
• Decimals - Expressions
→ Expression Simplification
→ PEMA / BOMA