
what you'll learn...
overview
Addition or Subtraction of decimals is explained. The following are explained for decimals.
• addition in first principles -- combining two quantities and measuring the combined
• subtraction in first principles -- taking away a part of a quantity and measuring the remaining quantity.
• Simplified procedure : Sign property of Addition and Addition by place value
• Simplified procedure : Sign property of Subtraction and Subtraction by place value
combine
Addition represents "putting-together" or "combining" of two quantities.
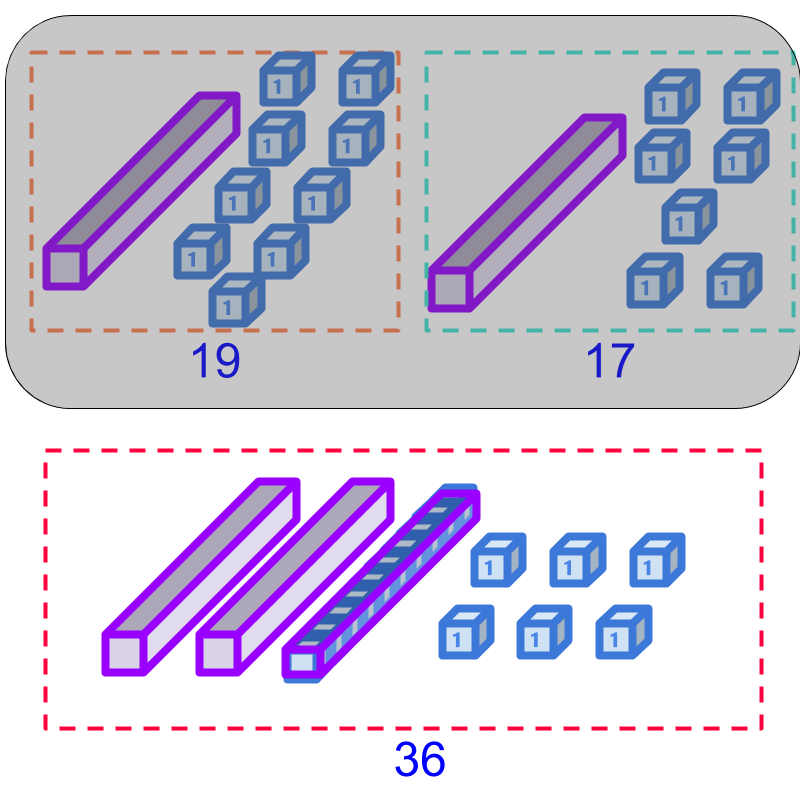
In whole numbers addition, We learned "regrouping" or "carry-over" -- " of a lower place-value can be grouped into of immediate higher place-value".
Addition of and is illustrated in the figure.
Addition of and is sum of ten, units, and ten units. This equals tens and units. units is regrouped into ten, making the sum as tens and units. In whole number form, it is .
In integer addition, we studied "sign-property of addition" -- "the positive and negative sign of the numbers are handled when adding the numbers".
take away
Subtraction represents "taking-away" or "removing" a number of quantities from another number.
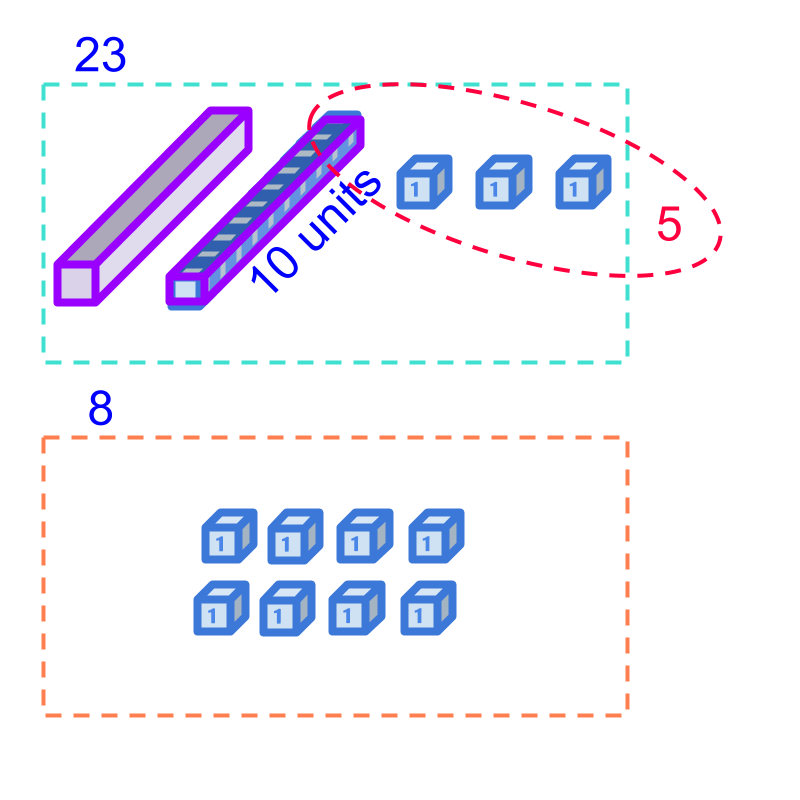
In whole numbers subtraction, we studied "de-grouping" or "borrowing" - " of a higher place-value can be split into of immediate lower place-value
Subtraction of from is illustrated in the figure.
Subtraction is taking away of ten, units, from tens units. To achieve that, ten (from minuend tens units) is de-grouped to units and added to the units. From the units, is taken away. The result is units.
In integer subtraction, "subtraction is handled as inverse of addition".
For example, to subtract from , the subtraction is modified into addition . The rules of addition are followed in this.
in integer form "". It is also given as .
in integer form is "". It is also given as .
Directed numbers, positive and negative, are explained as "aligned in direction" and "opposed in direction".
addition (recap)
In whole-numbers, integers, and fractions, we have learned addition of numbers.
Addition First Principles : Two numbers representing count or measurement are put-together and the combined quantity is counted or measured.
Addition by Place-Value with regrouping: The digits of corresponding place-value positions are aligned and added. At each place-value position, the sum is regrouped. This is called carry-over.
Sign-property of Addition : The signs of the addends are handled appropriately
• positive + positive is simple addition
• positive + negative is subtraction of the number with smaller absolute value from the number with larger absolute value. The sign of the sum is the sign of the larger absolute value.
• negative + negative is simple addition with negative as the sign of the sum.
subtraction (recap)
In whole-numbers, integers, and fractions, we have learned subtraction.
Subtraction First Principles : A number representing count or quantity is taken-away from another number and the remaining quantity is counted or measured.
Subtraction by Place-Value with de-grouping: The digits of corresponding place-value positions are aligned and subtracted. At each place-value position, the minuend is de-grouped if subtrahend is larger. This is called borrowing.
Subtraction of Integers : The subtraction is converted to addition of minuend and negative of subtrahend. The sign-property of addition is applicable.
Let us see the decimal addition and subtraction now.
simple examples
The sum of and is "".
represents counts of piece.
represents counts of piece.
Addition is combining the quantities and counting or measuring together.
Together, the quantities make counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
The difference is "".
represents counts of piece.
represents counts of piece.
Subtraction is taking-away an amount from another and counting or measuring the remaining.
The remaining makes counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
carry over in decimals
The sum of and is "".
represents count of piece and counts of piece.
represents count of piece and counts of piece.
Addition is combining the quantities and counting or measuring together.
Together, the quantities make counts of piece and counts of pieces. counts of pieces can be regrouped to count of pieces. This together makes, counts of pieces and counts of pieces, equaling in decimal.
taking away in decimals
The difference is "".
Subtraction is taking-away an amount from another and counting or measuring the remaining.
In the place, counts subtrahend is subtracted from counts minuend. Since minuend is smaller, count from immediate higher place value is de-grouped or borrowed to make minuend at place and at place .
Subtracting counts from counts, the different is counts in place.
Subtracting count from counts, the difference is count in place.
These two makes the difference as count in place and counts in place, equaling in decimal.
aligning place value in decimals
The sum of and is "".
represents count of whole and counts of piece.
represents count of piece.
Together, the quantities make count of whole and counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
The difference of is "".
The numbers are aligned at the corresponding place-value positions. By de-grouping or borrowing, the place of minuend is counts. Subtracting counts from that, the difference is counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
directed decimals
The sum of and is "".
Note that, positive and negative numbers are "aligned" and "opposed" directions in directed numbers.
represents aligned counts of piece.
represents opposed counts of piece.
Addition is combining the quantities and counting or measuring together. aligned and opposed make together is aligned.
Together, the quantities make aligned counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
The sum of is "".
Note that, positive and negative numbers are "aligned" and "opposed" directions in directed numbers.
represents opposed counts of piece.
represents aligned counts of piece.
When handling directed numbers, Subtraction is handled as inverse of addition (explained in integers).
Follow the decimal addition procedure.
Together, the quantities make opposed counts of piece, equaling in decimal.
decimal addition & subtraction
Decimal Addition - First Principles : The numbers representing quantities are combined together and the combined quantity is measured or counted.
Decimal Subtraction - First Principles : The subtraction is handled as addition of minuend and negative of subtrahend.
In decimal addition, the following are understood.
• handling the sign (positive or negative)
• adding at place-value of the digits
• the regrouping at digit level.
Let us look at the simplified procedure to add or subtract decimals.
addition by place-value
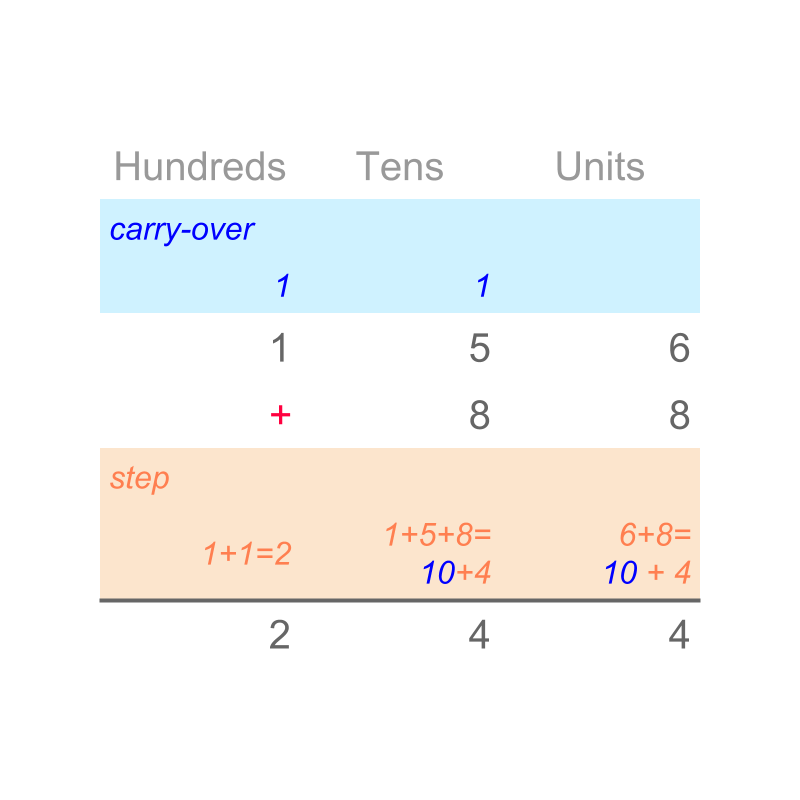
In whole numbers, we studied addition as combining two quantities. the simplified procedure for whole number addition is "Addition by place-value with regrouping".
An example is illustrated in the figure.
subtraction by place-value
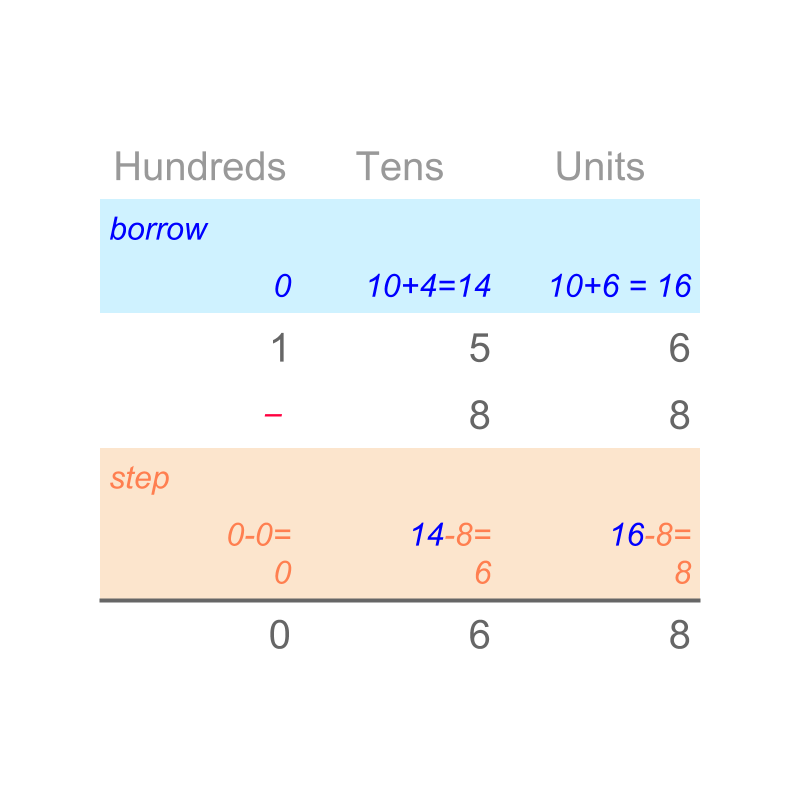
In whole numbers, we studied subtraction as removing an amount from a quantity. The simplified procedure for whole number subtraction is "Subtraction by place-value with de-grouping".
An example is illustrated in the figure. .
sign property of addition
In integers, we studied about addition of directed whole-numbers (that is, numbers with signs). The simplified procedure for integer addition is "sign-property of integer addition".
The sign-property of integer addition is given as
• positive + positive is whole number addition
• positive + negative is subtraction of the number with smaller absolute value from the other. The difference is the absolute value of the result. The sign of result is the sign of the number with larger absolute value.
• negative + negative is the sum of absolute values with negative sign.
This was explained in integers.
subtraction as inverse of addition
In integers, we studied about subtraction of directed whole-numbers (that is, numbers with signs). The simplified procedure for integer subtraction is "convert the subtraction to inverse of addition and then, add based on sign-property of integer addition".
.
place-value order
The extended place value order for decimals is " hundredth tenth units tens hundreds ".
simplify decimal addition
The sum of is "". By first principles, the values are combined and the combined quantity is counted.
A simplified procedure is designed to represent the addition by first principles.
The digits of the numbers are aligned by place-value. The digits are added in place-value.
The sum of
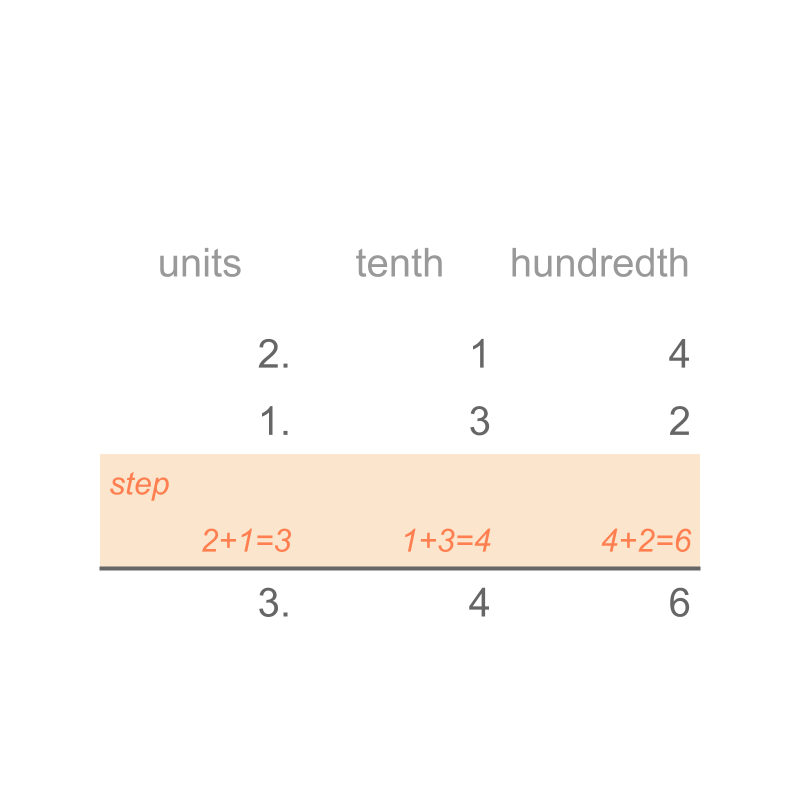
What is the sum of ?
The answer is "". By first principles, the values are combined and the combined quantity is counted. When a sum at a place value is greater than or equal to , it is regrouped to the immediate higher place-value.
A simplified procedure is designed to represent the addition by first principles.
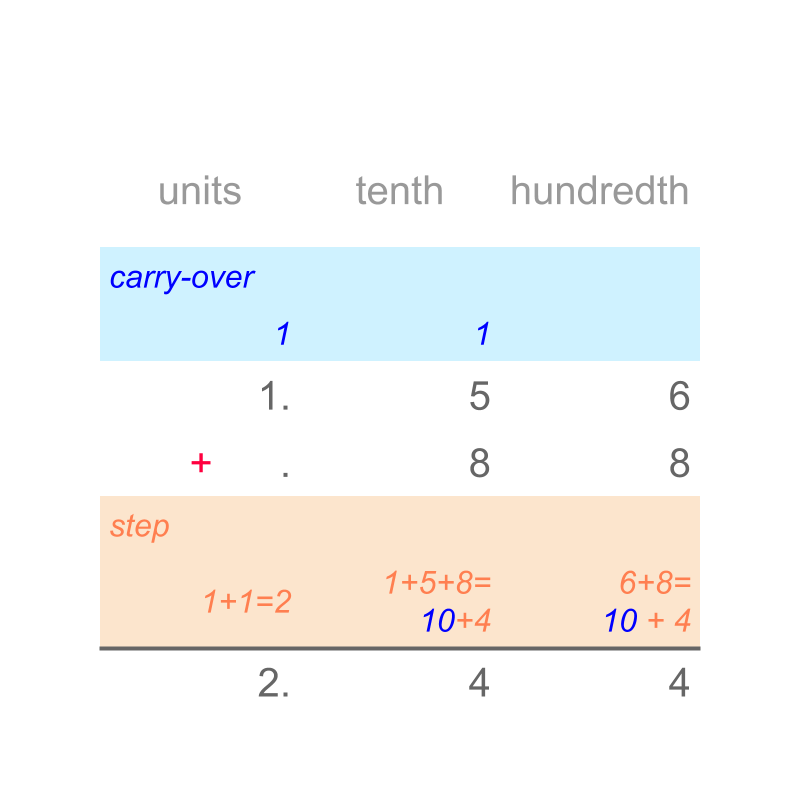
Consider the addition of .
The digits of the numbers are aligned by place-value. Note that of tenth place-value is aligned to of tenth place value. The digits are added in place-value starting from the lowest place-value hundredth. The result is regrouped to tenth and hundredths. This is repeated.
The sum of is "". The simplified procedure is given in figure.
simplify decimal subtraction
The difference is "".
By first principles, the subtrahend amount is taken-away from minuend and remaining is counted.
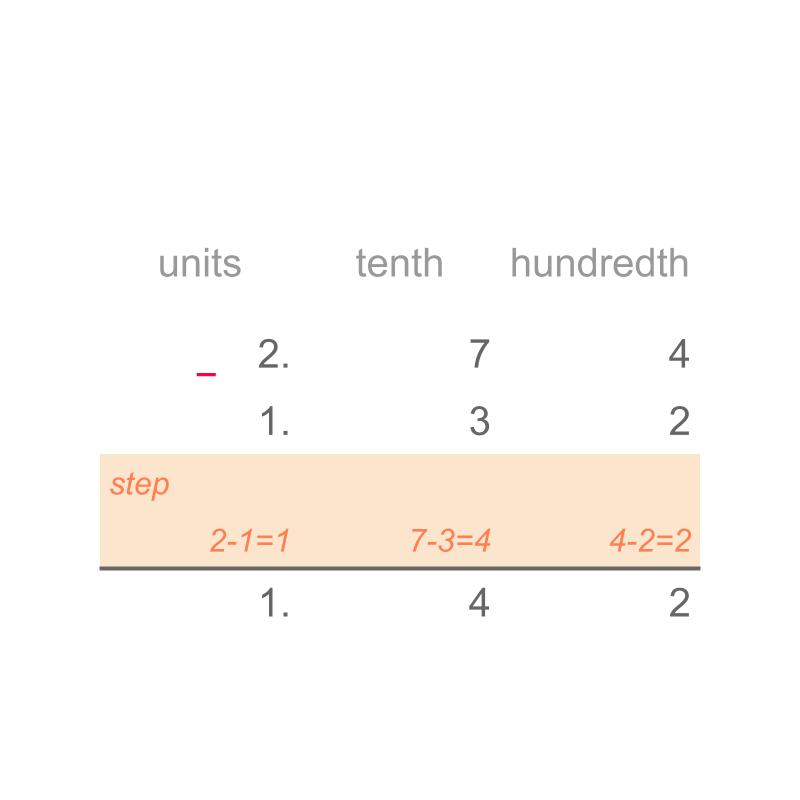
A simplified procedure is designed to represent the subtraction by first principles.
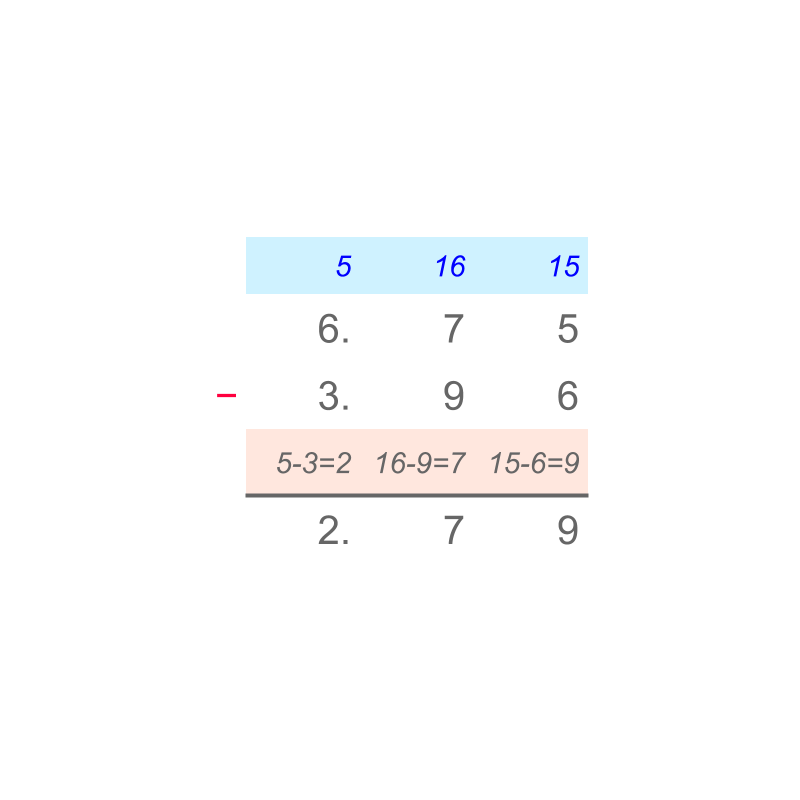
Consider the subtraction .
The digits of the numbers are aligned by place-value. The digits are subtracted in place-value. The simplified procedure is given in figure.
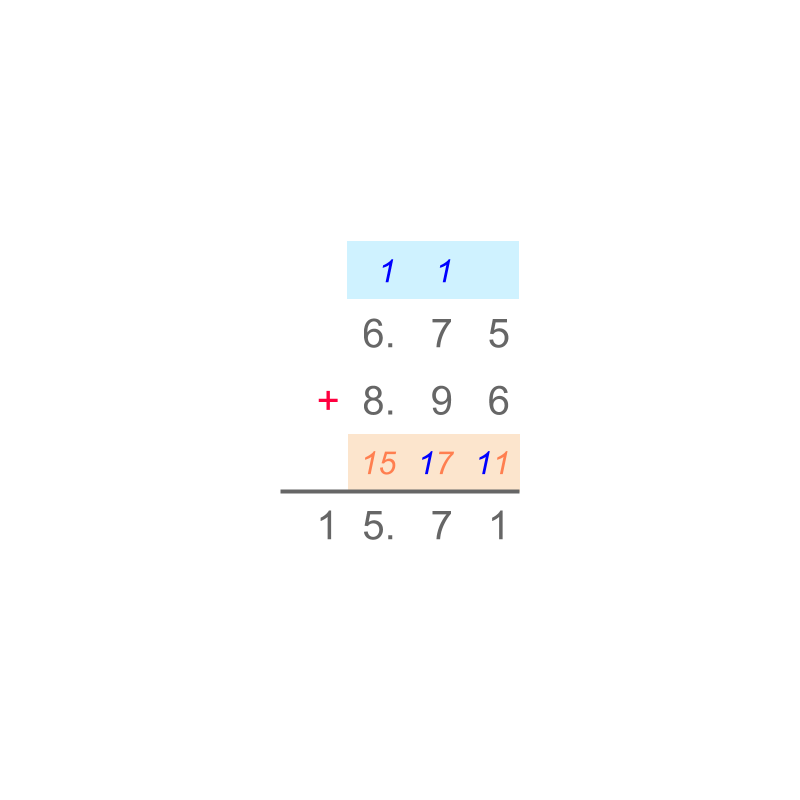
The difference is "".
By first principles, the subtrahend amount is taken-away from minuend. When subtrahend is greater than the minuend, the immediate larger place-value of minuend is de-grouped before subtraction.
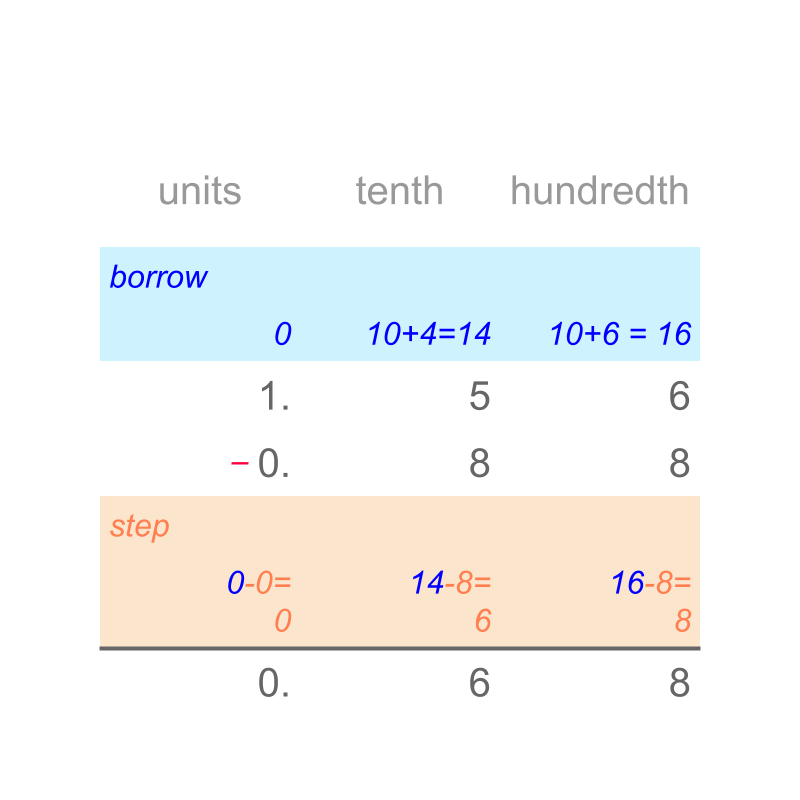
A simplified procedure is designed to represent the subtraction by first principles.
Consider the subtraction .
The digits of the numbers are aligned by place-value. Note that of tenth place-value is aligned to of tenth place value. The digits are subtracted in place-value starting from lowest place-value hundredth. The subtrahend count is larger than the minuend counts. This leads to de-grouping or borrowing before performing subtraction.
The difference is "". The simplified procedure is given in the figure.
simplification
Addition of Decimals Decimals are directed numbers with positive or negative sign.
The Sign-property of Integer Addition is applicable to Decimals
positive + positive is simple addition of absolute values
positive + negative is subtraction of smaller absolute value from larger one with result having sign of number with larger absolute value
negative + negative is simple addition of absolute values with result having negative sign.
The addition of absolute values is performed as per Addition by Place-value with regrouping.
The subtraction of absolute values is performed as per Subtraction by Place-value with de-grouping.
The extended place-value order for decimals is used.
hundredth tenth units tens hundreds
Subtraction of Decimals : Decimals are directed numbers with positive or negative sign. Subtraction is handled as addition of minuend and negative of subtrahend.
That is, the above procedure for addition is followed after converting subtraction to addition.
examples
Find the sum of and .
The answer is ""
Find the sum of and
The answer is ""
Find the sum of and
The answer is ""
Find the sum of and
The answer is ""
Find the difference .
The answer is ""
Find the difference of
The answer is ""
Find the difference
The answer is ""
Find the difference
The answer is ""
summary
Addition of Decimals Decimals are directed numbers with positive or negative sign.
The Sign-property of Addition is applicable to Decimals
positive + positive is simple addition of absolute values
positive + negative is subtraction of smaller absolute value from larger one with result having sign of number with larger absolute value
negative + negative is simple addition of absolute values with result having negative sign.
The addition of absolute values is performed as per Addition by Place-value with regrouping.
The extended place-value order for decimals is used.
hundredth tenth units tens hundreds
The subtraction of absolute values is performed as per Subtraction by Place-value with de-grouping.
Subtraction of Decimals : Decimals are directed numbers with positive or negative sign. Subtraction is handled as addition of minuend and negative of subtrahend.
That is, the above procedure for addition is followed after converting subtraction to addition.
Outline
The outline of material to learn "decimals" is as follows.
Note: goto detailed outline of Decimals
• Decimals - Introduction
→ Decimals as Standard form of Fractions
→ Expanded form of Decimals
• Decimals - Conversion
→ Conversion between decimals and fractions
→ Repeating decimals
→ Irrational Numbers
• Decimals - Arithmetics
→ Comparing decimals
→ Addition & Subtraction
→ Multiplication
→ Division
• Decimals - Expressions
→ Expression Simplification
→ PEMA / BOMA