
what you'll learn...
overview
This page formalizes the value of the digits in a number as follows.
• face value : the count represented by the digit.
eg: 22 has face value of 22 in 235235.
• place value : the value represented by the digit as part of the number.
eg: 22 has place value of 200200 in 235235.
Face and Place
We learned about representation of the number 721 in three forms. Let us revise that quickly.
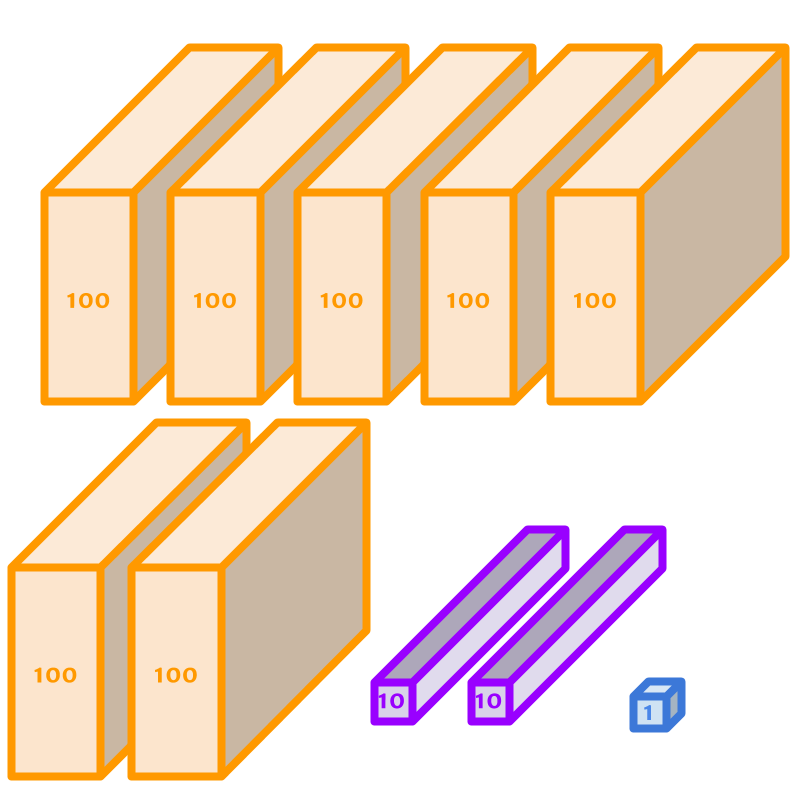
The number 721 is represented using blocks.
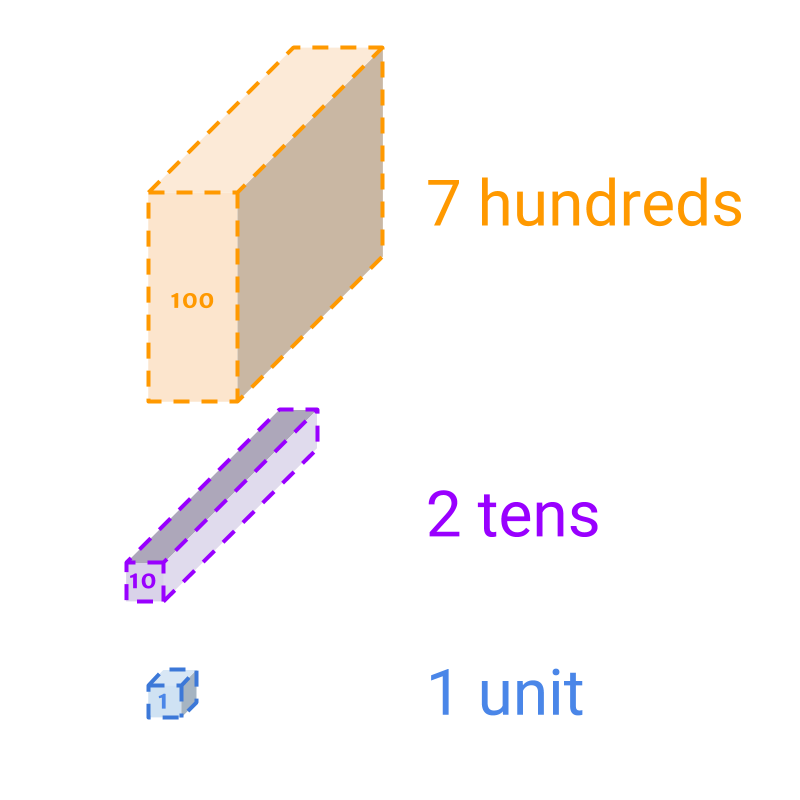
The number is represented using the count of each of the blocks. Instead of laying out all the blocks, the representation gives the count of each of the blocks. The blocks are of sizes 1, 10, and 100.
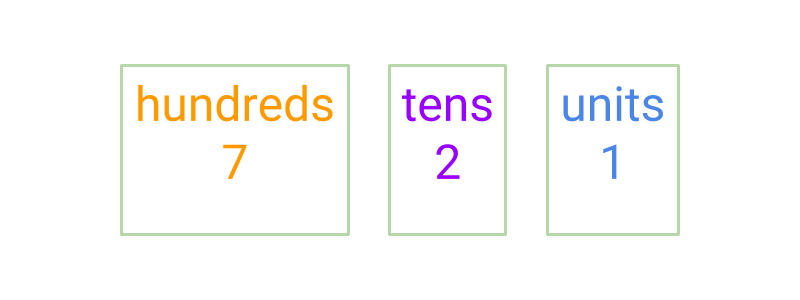
The number is represented without blocks. Instead of providing a pictorial representation of the blocks, the value is given in letters. The values are hundreds, tens, and units, equivalently representing blocks of size 100, 10, and 1.
The word "value" means: amount; measured amount; counted number.
The word "face", in face-value means: value represented by the symbol, without any context or details. That is, something is presented and taken as it is, without analyzing.
The word "place" in place-value means: a specific position or location.
Face Value: For a digit in a number, the face value is the value of the digit. Eg: 2 has face value of 2 in 235.
Place Value: For a digit in a number, the place value is the value taken by the digit as part of the number. Eg: 2 has place value of 200 in 235.
Some examples
The face value of 2 in the number 5234 is 2.
The place value of 2 in the number 5234 is 200.
The face value of 3 in 2341 is 3.
The place value of 2 in 6234 is 200.
The face value of 6 in 16425 is 6.
Summary
Face Value: For a digit in a number, the face value is the value of the digit. Eg: 2 has face value of 2 in 235.
Place Value: For a digit in a number, the place value is the value taken by the digit as part of the number. Eg: 2 has place value of 200 in 235.
Outline
The outline of material to learn whole numbers is as follows
Note: click here for detailed outline of Whole numbers
• Introduction
→ Numbers
→ Large Numbers
→ Expanded form
→ Face and place values
→ Approximation and Estimation
• Comparison
→ Comparing two numbers
→ Number line
→ Predecessor & Successor
→ Largest & Smallest
→ Ascending & Descending
• Addition Subtraction
→ Addtion: First Principles
→ Addition: Simplified Procedure
→ Subtraction: First Principles
→ Subtraction: Simplified Procedure
• Multiplication Division
→ Multiplication: First Principles
→ Multiplication: Simplified Procedure
→ Division: First Principles
→ Division: Simplified Procedure
• Numerical Expression
→ Introducing Numerical Expressions
→ Precedence
→ Sequence
→ Brackets