
what you'll learn...
overview
This page introduces addition of whole numbers as combining two quantities and counting or measuring the combined quantity.
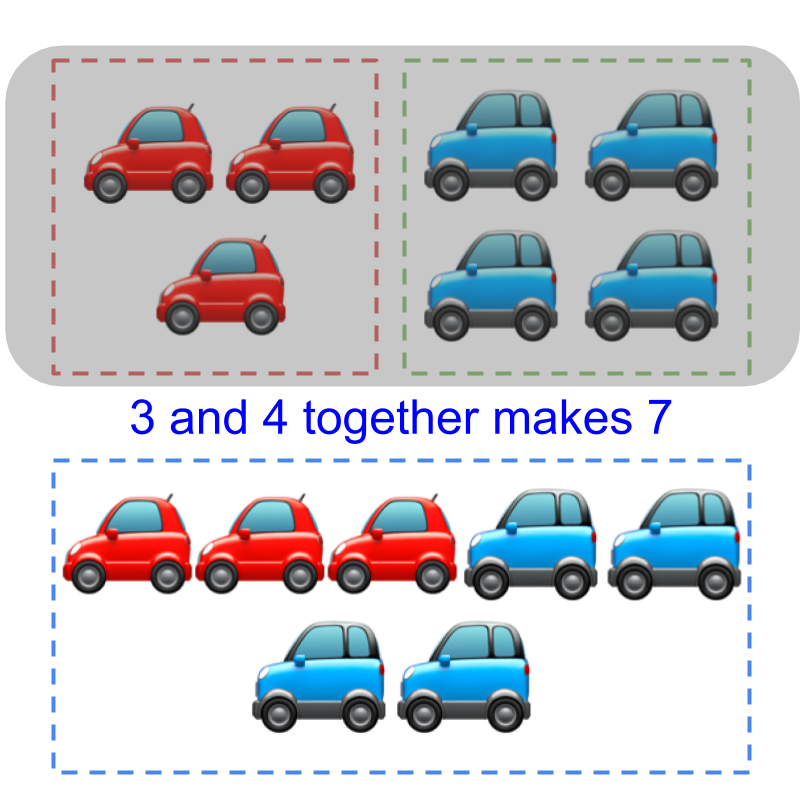 Counts of 33 and 44 are combined together and the counting is done from 11 to 77. The resulting count is 77
Counts of 33 and 44 are combined together and the counting is done from 11 to 77. The resulting count is 77
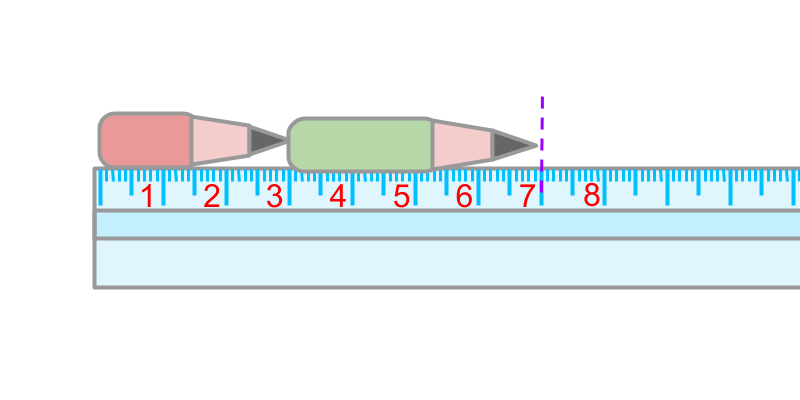 Measures of 33 and 4 are combined together. The measure of combined quantity is 7
Measures of 33 and 4 are combined together. The measure of combined quantity is 7
The same is abstracted for addition in number-line.
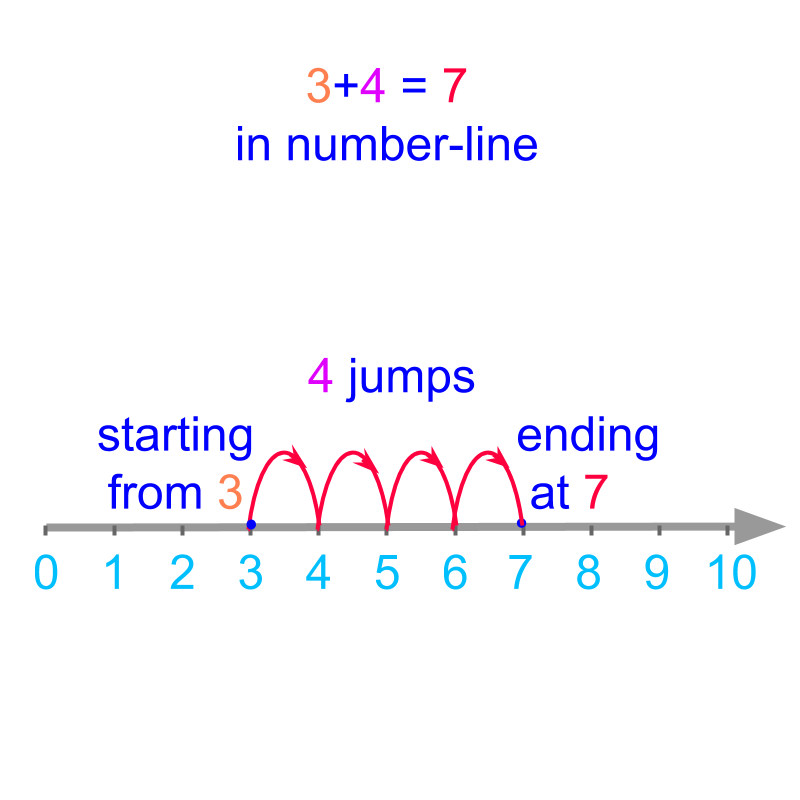 The definition of addition in first principles forms the basis to understanding the simplified procedure for addition of large numbers.
The definition of addition in first principles forms the basis to understanding the simplified procedure for addition of large numbers.
combine them
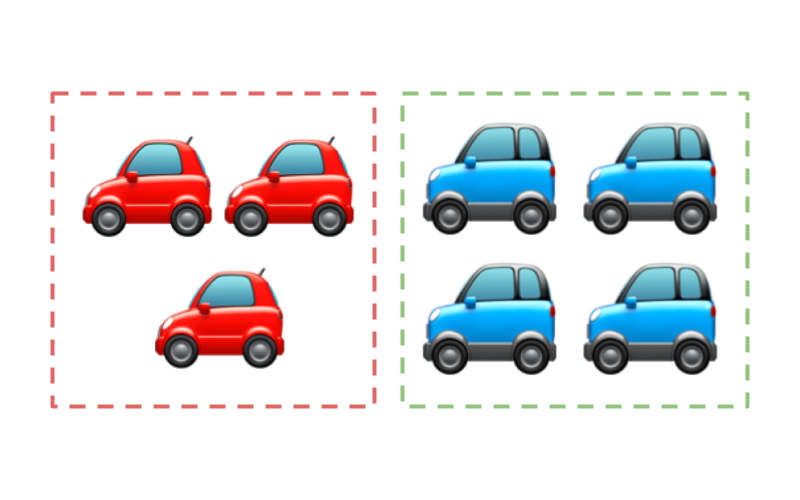
There are 3 red cars and 4 blue cars in the figure. These cars are

Considering the figure with 3 red cars and 4 blue cars. 3 and 4 are combined together and the counting is done from 1 to 7. The resulting count is 7.
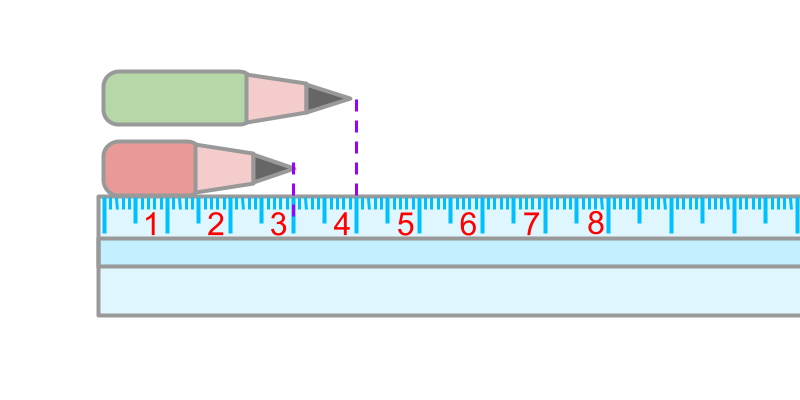
A red pencil is 3 centimeters in length. A green pencil is 4 centimeters in length.

The two pencils are
0 and the measure at the end is 7.
The count or measure of quantities can be combined or added.
The addition results in count or measure of the combined quantity.

Addition 3+4 is given in
addend and sum
The English word
Addition - First Principles : Two numbers are considered, each of which represents a count or measurement. The quantities represented by the numbers are combined to form a result representing a combined count or measurement. The combined count or measurement is the result of addition.
eg: 20 and 13 are combined together 20+13=33.
20 is an addend
13 is also an addend
33 is the sum
What is the sum of 4 and 2?
The answer is '6'.
summary
Addition - First Principles : Two numbers are considered, each of which represents a count or measurement. The quantities represented by the numbers are combined to form a result representing a combined count or measurement. The combined count or measurement is the result of addition.
eg: 20 and 13 are combined together 20+13=33.
20 is an addend
13 is also an addend
33 is the sum
Outline
The outline of material to learn whole numbers is as follows
Note: click here for detailed outline of Whole numbers
• Introduction
→ Numbers
→ Large Numbers
→ Expanded form
→ Face and place values
→ Approximation and Estimation
• Comparison
→ Comparing two numbers
→ Number line
→ Predecessor & Successor
→ Largest & Smallest
→ Ascending & Descending
• Addition Subtraction
→ Addtion: First Principles
→ Addition: Simplified Procedure
→ Subtraction: First Principles
→ Subtraction: Simplified Procedure
• Multiplication Division
→ Multiplication: First Principles
→ Multiplication: Simplified Procedure
→ Division: First Principles
→ Division: Simplified Procedure
• Numerical Expression
→ Introducing Numerical Expressions
→ Precedence
→ Sequence
→ Brackets